* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neural Basis of the Oblique Effect
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
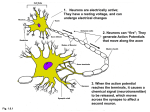
Neural Basis of the Oblique Effect Baowang Li, Matthew R. Peterson, Ralph D. Freeman What questions does the group ask and why does anyone care? • What is the neural basis of the oblique effect? • To make inferences about the architecture of the visual system in the brain. • Reconciliation of physiological data with a behavioral phenomenon. Alternative answers to problem 1. Number neurons tuned to horizontal and vertical vs. oblique orientations 2. Difference in tuning widths of neurons in V1 3. Difference in response (firing rate) to stimuli 4. Latency of response Alternatives continued 5. Width/shape of tuning curve (measurement: slope of tuning curves) 6. Type of cell 7. Effect exists outside of V1 (retina, LGN, V2) 8. Some combination of the above Methods • Shone an oriented light stimulus in the eye of anesthetized and paralyzed cats • Used microelectrodes to make recordings of single neurons in V1. • Classified cell as simple or complex. • Recorded: orientation preference, tuning curve, spatial frequency, firing rate of cells • Combined data from over 4,000 cells Results Fig 2 Fig 3 Fig 4 Fig 5B Results continued Fig 10 Fig 7A Fig 7A Fig 6 Conclusions • Combination of alternatives were confirmed: – The effect exists only for a subpopulation of cells: simple cells in V1 with high spatial frequency. – There are more cells tuned for cardinal orientations and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning curves are also steeper for horizontal orientations. • Response properties of individual neurons do not change: rate and latency. More Conclusions • The effect is based on the population of neurons in V1, not on changes in individual neurons. • Simple cells must directly project to higher areas in addition to/instead of only to complex cells. Problems? • Varying N value could be misleading • Did not look at any cells outside of V1 • Cats were anesthetized. It has been shown that anesthesia itself changes neuronal response properties. • Anesthesia also makes simultaneous psychophysics in animals impossible. Direction of causality unclear.