* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
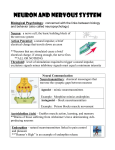
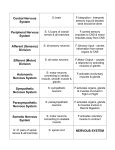
Nervous System Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. I. Division of the Nervous System A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. 2. B. Peripheral Nervous System( PNS) 1. Nervous that are outside the CNS a. b. 2. Sub divisions of the PNS a. (afferent)-conducts action potential from sensory receptors to the CNS. b. (efferent) – conducts action potential from CNS to PNS. (muscle or glands) a. - serves sensory nerves, receptors (skin) sensory organs (head) & motor nerves that stimulate the skeletal muscle voluntary nervous system b. - automatic 1. - involving stressful activities 2. - normal functioning II. Nerve Tissue A. - support & maintain neurons 1. - Provide insulation covering around large axons. 2. neurons - Anchor to blood capillaries. 3. - form & circulate cerebrospinal fluid. 4. - phagocytize invading microorganisms. 5. - insulation covering around the CNS. B. - functional unit of the nervous system 1. Structure a. - receive impulses b. - typical to other cells 1. - similar to RER 2. threads - network of fine c. (nerve fiber) - carries impulse away from the cell body. 1. One axon to every neuron 2. – side branches 3. – site of the axon missing Nissl bodies d. insulating barrier from a schwann cell around a axon. 1. Nourishment e. cytoplasm & nuclei of the schwann cell on the outer covering. f. - gaps where myelin sheaths are absent. g. gray matter h. white matter - 2. Types of Neurons a. - many dendrites (signal to muscles). b. - 1 dendrtie & axon (eyes, ears, & nose). c. d. Sensory (afferent) CNS. e. Association (interneurons) the CNS. f. Motor (efferent) CNS. 3. Function a. potential Polarized mv sodium ions the neuron than . potassium ions the neuron than . -this is maintained by the . -but due to the large ions stuck inside. b. potential – (excitable) Nerve impulse + mv – sodium moves into the cell – potassium moves outside the cell. C. period - hyperpolarized mv. Inside is more . Review Where do you find the following ions in relations to the neuron? chloride, sodium, potassium Why do they call it a sodiumpotassium pump? What is a threshold signal? 4. All or None Response a. - minimum strength that can cause an action potential. b. cannot initiate a response. - c. - series of subthreshold stimuli can have a cumulative effect. 5. Transmission of impulse a. Synapse b. Presynaptic c. Postsynaptic d. Synaptic end bulb e. Synaptic vesicles f. Neurotransmitters (50 different) 6. Excitatory vs. Inhibitory transmissions a. Excitatory causes a (more Na allowed to enter the postsynaptic) b. Inhibitory III. The Central Nervous System A. - Conduction pathway for impulses between the brain & the PNS, reflex center. Protected by . Compose of matter. Conduction pathway between the brain & nerves. Reflex center long. cm B. Protective coverings membrane layers. 1. - outermost, thick, & tough. - space filled with fat between the bone & dura matter. 2. - middle layer of collagen fibers. Subarachnoid space filled with Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) - shocking absorning & transporting. 3. - inner most, attached to the spinal cord. C. Structures 1. segments each with a pair of spinal nerves. 2. - center of the cord (looks like an H). a. terminal endings of sensory neurons. b. - motor neurons of the autonomic nervous system. c. - motor neurons to skeletal muscle. 3. - Surrounds the gray matter a. Anterior Columns b. Lateral Columnsc. Posterior Columns - D. Conduction Pathways 1. - sensory info to the brain. 2. - motor info from the brain. neurons to the effectors. E. Spinal nerves 1. Mixed nerves because they contain both sensory and motor neurons. 2. Organizied into regions that they emerge. C– T– L– S– Co – 3. Plexus – nerves come together and separate. a. three main ones cervical c1-c4 brachial – c5-t1 lumbosacral – l1-s4 E. Reflex Center 1. Reflex is an way of responding to an emergency situation. a. at the end of the sensory neuron. b. neuron to the CNS Associated neuron in the spinal cord (reflex center). c. Motor 2. Types of reflexes a. - actions involve skeletal muscles. 1. Withdrawal – protective 2. Pattellar - knee jerk (2 neurons, sensory to the motor) 3. Stretch reflex b. - smooth & cardiac to maintain homeostasis. 1. Breathing, vomiting, sneezing, & coughing IV Brain - integrative center of the nervous system billion neurons. One of the largest internal organs. A. Protective coverings - Meninges membrane layers. 1. thick, & tough. - outermost, - space filled with fat between the bone & dura matter. 2. - middle layer of collagen fibers. Subarachnoid space filled with Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shocking absorbing & transporting. 3. - inner most, attached to the spinal cord B. Cerebrum “ Largest structure in the brain ”- 1. Cerebral hemispheres 2. Convolutions - upwards folds - inward folds 3. Fissures 4. Four lobes a. – smell, motivation, aggression, mood. b. – touch, pain, temperature, balance, taste c. – sight d. – smell, hearing, memory 5. Sensory Functions a. small portion of the sensory input results in sensation. b. – sends signals to the brain. -each tract is limited ex… ex. Lateral spinothalamic tract pain & temperature. ex. Dorsal column touch, position, pressure -most tracts have 2 or 3 neurons to the brain. -almost all end in the thalamus. C. – between brain stem & cerebrum 1. - relay station for sensory impulses (except smell) entering the brain. 2. – pineal body (puberty) 2. - Primary control for the autonomic nervous system (homeostasis). a. Thermostat control for body temp b. regulates food & water uptake c. maintain walking & sleeping patterns. d. associated with emotion (rage, aggression, sex drives 1. Pituitary glands - endocrine glands D. - reflexes for rapid eye, head & trunk movements E. - Bridges the cerebrum & cerebellum F. - part of the brain stem & most inferior brain structures 1. Cardiac & respiratory center G. - sends signals to the skeletal muscles Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves V. Disorders A. – inflammation of the brain B. – inflammation of the meninges. C. – viral disease transmitted by saliva of a animal bite. D. – bacterial disease that produces a neurotoxin that affect lower motor neurons in the spinal cord & brain stem. E. – autoimmune disorder caused by a viral infection F. – general, defects in motor functions from several types of brain damage or birth related injury. G. – muscular rigidity, lack of movement H. I. – mental deterioration (dementia). J. – group of brain disorders that cause seizures K. - shingles VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decreases, but other neurons can compensate for this loss. D. Short term (problem solving, thinking) memory decreases slowly until the age of 60. Afterwards increase rate of memory loss, especially after 70. E. Long term memory seems to be unaffected. F. More time to fall asleep, more walking periods during the night, and longer amount of time being awake at night. G. Many older people shoe no change and some show a 10% increase in thinking ability due to education, health, motivation.