* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
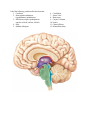
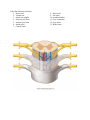
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures make up the brainstem, what is the function of each? 3. What structures make up the diencephalon, what is the function of each? 4. What are the four ventricles and what is their function? 5. What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)? 6. Describe the following about the CSF a. Where is it made. b. How is it made CSF. c. What is the path it takes through the brain and spinal cord. 7. What are the 5 lobes of the brain, what are they named after, what functional regions are found in each? 8. Define the following: a. Sulcus b. Gyrus c. Fissure 9. What major structure separates the left cerebral hemisphere from the right? 10. What major structure separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum? 11. Describe the following anatomical structures: a. Central sulcus b. Precentral gyrus (what is its function) c. Postcentral gyrus (what is its function) 12. Describe the path of motor control from the brain to skeletal muscle. Be sure to include the basal ganglia and cerebellum’s role in addition to the primary motor and premotor cortex. Be able to locate upper and lower motor neuron (where does each start and end). Be able to follow the path a motor response takes through the brain and out to the muscle. 13. What is the function of the following cerebral cortices, what cerebral lobe are they found in? a. Primary somatosensory cortex/ somatosensory association area b. Primary visual cortex/visual association area c. Auditory cortex/ association area d. Olfactory cortex e. Gustatory cortex f. Frontal Eye Field g. Wernikies Area h. Brocas Area 14. How do the primary cortices and association areas work together? 15. What is the function of the limbic system? 16. What is the function of the reticular system? 17. Describe the pathway of incoming sensory information. Include first, second and third order neurons including location of cell bodies and axon terminals. 18. Describe the pathway of outgoing motor commands. Include upper and lower neurons including location of cell bodies and axon terminals. 19. What is the function of the following fiber tracts a. Projection fibers b. Commissural fibers c. Association fibers 20. A fly just landed on your arm. Describe how the signal travels from the arm, to the brain. What areas of the brain process the information, and what parts of the brain send a response to move your arm. Know the function of the following areas of the brain Region Function Basel Nuclei/Basel Ganglia Subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone, coordination of learned movement patterns. May initiate motor movement. Provides general pattern of rhythum for undergoing movements. Cerebrum Cerebellum Corpora quadrigemina (superior and inferior colliculus) Hypothalamus Limbic System (a functional group - not an anatomical structure) Mammillary bodies Medulla oblongata Pons Thalamus Ventricles Logic, learning & memory, “conscious” brain. Body posture, fine tune movements Process visual and auditory sensations Thirst, hunger, emotion, hormone production. Control of autonomic function, secretion of hormones. Establishes emotional states, links conscious, intellectual functions of cerebral cortex, facilitates memory storage and retrieval. Control of feeding reflex (chewing, licking, swallowing) Breathing, heart rate, visceral activities, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Higher levels of respiratory control, sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves Acts as a filter for ascending sensory information that is projected to the primary cortex and basal nuclei. Filled with CSF 21. Describe the anatomy spinal cord, include the following items: a. Cervical enlargement b. Lumbar enlargement c. Conus medullaris d. Cauda equina e. Filum terminal f. White matter g. Grey matter 22. What can be found in each of these anatomical structures? a. Anterior, posterior and lateral grey horn b. Dorsal and ventral roots c. Dorsal root ganglia. d. Central canal 23. Describe the following structures: a. Epidural space b. Denticulate ligament 24. Describe the three meninges found in the spinal cord. 25. Describe the anatomy of a typical peripheral nerve. Include the following: a. Axon b. myline c. fasicles d. endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium. 26. What is a ganglia? A nucleus? A fiber tract? 27. What is meant by a mixed nerve? 28. Describe the pathway of incoming sensory information to the spinal cord, and outgoing motor information from the spinal cord to the periphery. Include the location of cell bodes and axons of neurons within the following structures of the spinal cord: a. Dorsal root, ventral root, dorsal root ganglia b. Posterior grey horn, anterior grey horn c. Spinal nerve Label the following, and describe their function: 1. Cerebrum 2. Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus) 3. Mid brain (corpora quadrigemina, superior coliculi, inferior clliculi) 4. Pons 5. Medula oblongata 6. Cerebellum 7. Arbor Vitae 8. Brain stem 9. Corpus Collosum 10. Fornix 11. Choroid Plexus 12. Mammillary body Label the following structures: 1. Dorsal root 2. Ventral root 3. dorsal root ganglia 4. Posterior grey horn 5. Anterior grey horn 6. Spinal nerve 7. Central Canal 8. Dura mater 9. Pia mater 10. Arachnoid mater 11. Grey commisure 12. Grey mater 13. White mater Multiple Choice 1. The somatosensory cortex is found here: A. Pons B. Diencephalon C. Medulla D. Occipital lobe E. None of the above 2. The grey matter of the spinal cord is dominated by: A. Unmyelinated axons B. Cell bodies of neurons, neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons C. Schwan cells and satellite cells D. Myelinated axons 3. A synapse is: A. A junction between a neuron and a cell B. Site of neuronal communication C. Site of neurotranmitter release D. Separated by a synaptic cleft E. All of the above True/False 1. Grey matter mainly contains bundles of axons. 2. The ventral root of the spinal cord contains bundles of sensory axons. 3. Projection fiber tracts connect the left and right cerebral hemispheres.