* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
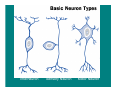
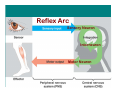
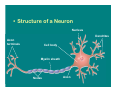
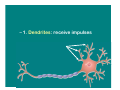
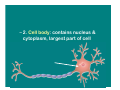
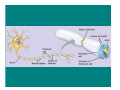
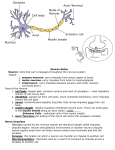
The Nervous System & Neurons Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments Overview of the Nervous System • The ultimate control of all the organ systems is done by the nervous system. A. Neurons • Neurons are nerve cells that carry electrical impulses through the body • Impulse = message • Neurons are classified according to the direction an impulse travels. • 3 Types of Neurons – 1. Sensory: carry impulses from sense organs to the brain – 2. Motor: carry impulses from the brain to muscles & glands – 3. Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and process impulses Interneuron Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron Reflex Arc Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron • Structure of a Neuron Nucleus Dendrites Axon terminals Cell body Myelin sheath Nodes Axon – 1. Dendrites: receive impulses – 2. Cell body: contains nucleus & cytoplasm, largest part of cell – 3. Axon: transmit impulses away from cell body – 4. Myelin Sheath: covering that insulates the axon, sending the impulse faster and gives axon a whitish appearance – Neurons with axons that have myelin make up “white matter” in the brain, while neurons without myelin are called “gray matter” – 5. Nodes: gaps in the myelin sheath where membrane is exposed – Impulses jump from one node to the next – 6. Axon terminals: transmits impulse (message) to next cell