* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Nervous System
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
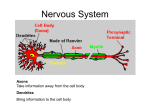
The Human Nervous System Major Organs Brain, Spinal Chord, Nerves Major functions • Sensory – Millions of sensory receptors detect changes, called stimuli, which occur inside and outside the body. • Integration – Decisions that are made based on the sensory input. • Motor – The response of the nervous system by sending signals to muscles, causing them to contract, or to glands, causing them to produce secretions. The Neuron ~functional unit of the nervous system! All neurons have 3 main parts: 1. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. Types of Neurons • Neurons can also be classified by the direction that they send information. – Sensory (or afferent) neurons: send information from sensory receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system. – Motor (or efferent) neurons: send information AWAY from the central nervous system to muscles or glands. – Interneurons: send information between sensory neurons and motor neurons. Most interneurons are located in the central nervous system. Neuron Communication • Neurons communicate with each other through the use of neurotransmitters. • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon into the synaptic cleft between an adjacent axons dendrite Pathway of a Nerve Stimulus Tip of axon releases neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft Dendrite receives stimulus (impulse) Axon takes impulse away from the cell body Impulse travels through the cell body CNS & PNS Central Nervous System & Peripheral Nervous System Nervous System Regulation • The sympathetic & parasympathetic systems are in control of the major organs of the body. Common Nervous System Diseases Depression & Addictions (neurotransmitters) Alzheimer’s & Schizophrenia (physiology) Carpel Tunnel & Spina Bifida (nerves) Bacterial & Viral disease Rabies is spread by infected saliva that enters the body through a bite or broken skin. The virus travels from the wound to the brain, where it causes swelling, or inflammation, and if untreated…death Haemophilus influenzae , Streptococcus neumoniae, group B Streptococcus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Neisseria meningitidis can all cause meningitis. Symptoms include brain damage, hearing loss, learning disabilities and possible death. It is spread through secretions, air and contaminated food. Career Opportunities • • • Child Neurology - specializes in the diagnosis and management of neurologic conditions in children. Clinical Neurophysiology- A neurologist who specializes in the diagnosis and management of central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous system disorders using a combination of clinical evaluation and electrophysiologic testing such as electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies (NCS), among others. Pain Medicine - provides a high level of care, either as a primary physician or consultant, for patients experiencing problems with acute, chronic or cancer pain in both hospital and ambulatory settings. Drugs & the Nervous System Nicotine causes the nervous system to become more sensitive & stimulated. This leads to short term effects: – increase in blood pressure – heart rate – faster respiration constriction of the arteries. Long-term effects of smoking on the nervous system are quite dangerous. People who smoke are more susceptible to cancers and muscular sclerosis. Drugs, continued Anabolic Steroids have many effects on many different organ systems. For the nervous system, steroids cause an increase in aggression ~ “Roid Rage”, irritability and severe fluctuation in moods. Users can also develop a dependency on this drug ~ they can become addicted. Users are also at an increased risk of committing suicide because of severe depression caused by steroid use. Drugs, Continued Alcohol has profound effects on neurons and the nervous system. Alcohol: • Impairs memory, judgment & reasoning • Depresses the actions of the Central Nervous System; therefore, decreasing reaction times and vital organ function. • Causes neuropathy, dementia, Wernicke's encephalopathy and clinical depression • Can lead to suicide and sleep disorders Drugs, continued Methamphetamine is a stimulant that causes actual physical changes to the brain. It effects the level of dopamine in the brain and is highly addictive. Stimulants will increase the activity of the Central Nervous System Anxiety, confusion, insomnia, depression and mood disturbances and displays of violent behavior are common with “meth” use. Psychotic episodes are prevalent, such as paranoia, hallucinations and delusions.