* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
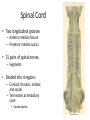
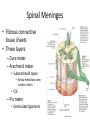
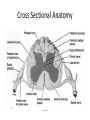
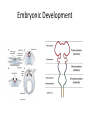
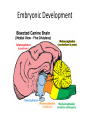
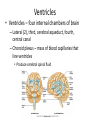
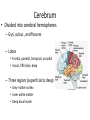
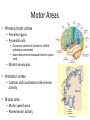
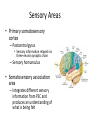
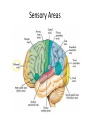
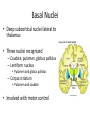
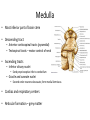
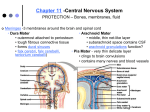
Ch. 13 The Central Nervous System Objectives • Be able to identify the various features of the spinal cord • Be able to identify the major parts of the brain and their functions • Understand how tracts and nuclei are arranged along the brain stem The Spinal Cord • Extends form the foramen magnum to L1 or L2 – About 42 cm long and 1.8 cm thick • Three main functions – Conduction • Conducts information up and down the cord, to and away from the brain and other regions of the trunk – Locomotion • Central pattern generators – Reflexes • Spinal reflexes involuntary response to a stimuli Spinal Cord • Two longitudinal grooves – Anterior median fissure – Posterior median sulcus • 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Segments • Divided into 4 regions – Cervical, thoracic, lumber, and sacral – Terminates at medullary cone • Cauda equina anatomyatlases.org Spinal Meninges • Fibrous connective tissue sheets • Three layers – Dura mater – Arachnoid mater • Subarachnoid space – Below medullary cone, lumbar cistern • CSF – Pia mater • Denticulate ligaments daviddarling.info Cross Sectional Anatomy d.umn.edu Spinal Tracts • Ascending tracts – Carry sensory information up • Descending tracts – Carry motor output down • Decussation – Contralateral – Ipsilateral • Sensory info typically carried by three neurons • Motor info carried by two neurons withealth.net Overview of the Brain • Control center of the body – Composed of an abundance of neurons • Divided into three major regions – Cerebrum • Divided into left and right hemispheres by longitudinal fissure – Gyri, sulci, – Communicate via the corpus callosum – Cerebellum • Posterior and inferior to the cerebrum • Second largest part of the brain – Brain stem • What remain of the brain if the cerebrum and cerebellum are removed – Diencephalon, midbrain, pons , and medulla Grey and White Matter • Arranged opposite of the spinal cord arrangement – Cortex composed of grey matter – Deep nuclei as well – Rest of brain is white matter running in tracts Embryonic Development niaaa.nih.gov Embryonic Development Meninges • Dura mater – Composed of two layers • Periosteal layer • Meningeal layer – Dural sinuses » Superior sagittal » Transverse • Arachnoid mater • Pia mater health.allrefer.com Ventricles • Ventricles – four internal chambers of brain – Lateral (2), third, cerebral aqueduct, fourth, central canal – Choroid plexus – mass of blood capillaries that line ventricles • Produce cerebral spinal fluid faculty.irsc.edu Cerebral Spinal Fluid • Clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the CNS – Contains more Na+ and Cl- than plasma • Reabsorbed by the subarachnoid villi • Three functions – Buoyancy – Protection – Chemical stability Blood Brain Barrier • Brain require significant supply of blood – Oxygen and glucose • Exposure to blood would make it susceptible to harmful agents • Blood-Brain barrier – Tight junctions between endothelial cells of brain capillaries – Permeable to water, glucose, O2, alcohol, anesthetics • Blood-CSF barrier – Tight junctions between ependymal cells of choroid plexus Cerebrum • Divided into cerebral hemispheres – Gyri, sulcus , and fissures – Lobes • Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital • Insula, fifth lobe, deep – Three regions (superficial to deep) • Grey matter cortex • Inner white matter • Deep basal nuclei emc.maricopa.edu Cerebral Cortex • The “boss” – Allows us to feel, move (voluntary), communicate, remember and understand • Grey matter – Cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons – No nerve tracts • Three kinds of functional regions – Motor areas – voluntary movement – Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensations – Association areas – integrate different info for purposeful action Motor Areas • Primary motor cortex – Precentral gyrus – Pyramidal cells • Conscious control of precise or skilled voluntary movement • Axons become corticospinal tract in spinal cord – Motor homunculus • Premotor cortex – Controls and coordinates skilled motor activity • Brocas area – Motor speech area – Planed motor activity thebrain.mcgill.ca Sensory Areas • Primary somatosensory cortex – Postcentral gyrus • Sensory information relayed via three-neuron synaptic chain – Sensory homunculus • Somatosensory association area – Integrates different sensory information from PSC and produces an understanding of what is being felt Sensory Areas Association Areas • Prefrontal cortex – Involved with intellect, cognition, recall, judgment, consciousness, reasoning, and personality • Language area – Wernicke’s area • Sounding unfamiliar words • Visceral association area – Cortex of insula – Conscious perception of visceral sensations Cerebral White Matter • Responsible for communication within cerebral areas and between cortex and and lower CNS – Myelinated axons that form tracts • Classified based on direction they run in – Commissural tracts • Enable communication between hemispheres – Corpus callosum – Association tracts • Connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Long, different lobes – Short, different gyri – Projection tracts • Connect cerebrum to lower brain and cord centers • Internal capsule – dense band of tracts between thalamus and basal nuclei • Corona radiata – fanning out of band Basal Nuclei • Deep subcortical nuclei lateral to thalamus • Three nuclei recognized – Caudate, putamen, globus pallidus – Lentiform nucleus • Putamen and globus pallidus – Corpus striatum • Putamen and caudate • Involved with motor control scienceblogs.com The Diencephalon • Consists of three paired structures – Thalamus • Relay to the cerebral cortex • Key role in motor control – Hypothalamus thebrainwiki.com • Major control center of autonomic and endocrine systems • Hormone secretion, autonomic effects, thermoregulation, food and water intake, memory – Epithalamus • Pineal gland The Brain Stem • Three regions: midbrain, pons, and medulla • Midbrain – Cerebral peduncles • Descending corticospinal tract – Cerebral aqueduct – Tectum – posterior to aqueduct • Corpora quadrigemina nuclei orble.com – Superior colliculi – coordinate head and eye movements – Inferior colliculi – auditory relay, reflexive response to sounds – Sustancia nigra – inhibitory motor center • Rich in melanin, precursor to dopamine – Red nucleus – fine motor control • Connects with cerebellum – includes nuclei of oculomotor and trochlear nerves Pons • Bulging brain stem region between midbrain and medulla • Consists of tracts • Nuclei of trigeminal, abducens, and facial nerves • Respiratory centers Medulla • Most inferior part of brain stem • Descending tract – Anterior corticospinal tracts (pyramidal) – Tectospinal tracts – motor control of neck • Ascending tracts – Inferior olivary nuclei • Send proprioceptive info to cerebellum – Gracile and cuneate nuclei • Second order neurons decussate, form medial lemniscus • Cardiac and respiratory centers • Reticular formation – grey matter Cerebellum • Located dorsal to medulla and pons – Connected via cerebellar peduncles • Cerebellar features – – – – hemispheres connected via vermis Gyri called folia Three lobes: anterior, posterior, flocculonodular Arbor vitae – white matter • Functions – Coordinated body movements and maintaining equilibrium