* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development and Plasticity of the Brain
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
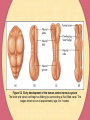
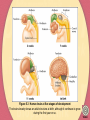
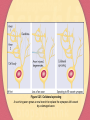
Chapter Five Development and Plasticity of the Brain Development of the Brain Growth and Differentiation of the Vertebrate Brain Early Beginnings CNS begins to form at two weeks gestation Development of the neural tube (figure 5.2) At birth, brain weighs 350g, at one year 1,000g Growth and Development of Neurons Proliferation-production of new cells Migration-move toward final destination Differentiation-form axons and dendrites Myelination-addition of insulating sheath Figure 5.2 Early development of the human central nervous system The brain and spinal cord begin as folding lips surrounding a fluid-filled canal. The stages shown occur at approximately age 2 to 3 weeks. Figure 5.3 Human brain at five stages of development The brain already shows an adult structure at birth, although it continues to grow during the first year or so. Video Development of the Brain Determinants of Neuron Survival Must make correct connections Must receive support from nerve growth factor neurotrophins act in several ways early in development cause cells to survive and grow increase the branching of incoming axons decrease pain and increase regrowth of damaged axons apoptosis-programmed cell death that occurs when connections are not reinforced Competition Among Axons as a General Principle We produce redundant synapses the most successful axons and combinations survive Development of the Brain Pathfinding by Axons Chemical Pathfinding by Axons Example: Weiss and the grafted salamander leg Specificity of Axon Connections Example: Sperry and the rotated eye of newt Chemical Gradients cell surface molecule chemical attractants Neurotrophins Figure 5.7 Summary of Sperry’s experiment on nerve connections in newts After he cut the optic nerve and inverted the eye, the optic nerve axons grew back to their original targets, not to the targets corresponding to the eye’s current position. Development of the Brain Fine-Tuning by Experience Effects of Experience on Dendritic Branching Enriched environments increase dendritic branching Generation of New Neurons stem cells in the interior of the brain scientists have observed new cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex Development of the Brain Effects of Experience on Human Brain Structures Example: music training on temporal lobe development Example: somatosensory cortex in violin players Combinations of Chemical and Experiential Effects Development of the Brain The Vulnerable Developing Brain Fetal Alcohol Syndrome decreased alertness, hyperactivity, varying degrees of mental retardation, motor problems, heart defects, and facial abnormalities Fetal Nicotine Exposure low birthweight, SIDS, decreased intelligence, hyperactivity Fetal Cocaine Exposure decrease in IQ and language skills Recovery of Function After Brain Damage Causes of Human Brain Damage closed head injury-sharp blow to the head resulting from a fall, an automobile accident, a sports accident, an assault, or other sudden trauma that does not actually puncture the brain stroke-loss of normal blood flow to a brain area ischemia-blood clot or other obstruction closes an artery hemorrhage-when an artery ruptures tissue plasminogen activator-breaks up blood clots Figure 5.20 Mechanisms of neuron death after stroke Procedures that can preserve neurons include removing the blood clot, blocking excitatory synapses, stimulating inhibitory synapses, blocking the flow of calcium and zinc, and cooling the brain. Recovery from Brain Damage Adjustments and Potential Recovery After Brain Damage Learned Adjustments in Behavior-making better use of unimpaired abilities Diaschisis-decreased activity of surviving neurons after other neurons are damaged The Regrowth of Axons peripheral axons can regrow axons will only regrow very short distances axons regrow better in the young Recovery from Brain Damage Adjustments and recovery cont’d Sprouting-when nearby, uninjured cells form new branches to the vacant synapses Denervation Supersensitivity-heightened sensitivity to a neurotransmitter after the destruction of an incoming axon Reorganized Sensory Representations and the Phantom Limb Effects of Age Older people do not recover as well as younger people, although, there is a delicate balance here because the very young brain is also more vulnerable Figure 5.25 Collateral sprouting A surviving axon grows a new branch to replace the synapses left vacant by a damaged axon. Figure 5.27 Demonstration of denervation supersensitivity Injecting 6-OHDA destroys axons that release dopamine on one side of the brain. Later amphetamine stimulates only the intact side of the brain because it cannot cause axons to release dopamine on the damaged side.Apomorphine stimulates the damaged side more strongly because it directly stimulates dopamine receptors, which have become supersensitive on that side. Recovery from Brain Damage Therapies Behavioral Interventions Physical therapy Occupational therapy Speech therapy Drugs Nimodipine-prevents calcium from entering cells gangliosides-promote the restoration of damaged brains through unknown mechanisms progesterone-women with brain injury recover better than men and especially if the damage occurs when progesterone levels are high during their cycle Recovery from Brain Damage Therapies Brain Grafts Used for Parkinson’s Disease Currently Experimental