* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Research Methods
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Electroencephalography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoencephalography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
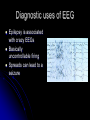
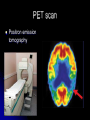
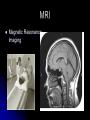
Research Methods Psychology 2617 Or, so how do we know this stuff We can look at the whole brain We can look at parts thereof We can look at neurons We can look at synapses neurons Even before electron microscopes, we could look at neurons thanks to Golgi He discovered that when stained with Silver chromate, neurons went black Today we call this golgi stain Led to the classification of neurons, as we could finally see their physical properties Stains are not always bad Golgi stain does not show number of neurons in a region that well though It stains just a few Nissl Used dyes! Methelyne blue Myelin staining HRP and axonal transport allow us to see circuits! Radiation, run for your lives! X Rays are cool, but, they don’t work well on brains AEG, kinda dangerous CAT scans are cool though Gives us a good idea about form Some of this stuff is a little, oh yucky Angiography Wada technique Both involve injections into the blood supply of the brain while the patient is awake Wada technique proved once and for all the idea of hemispheric specialization EEG Electroeds placed on the head Brain waves Gamma activity is fast and big, peak activity Beta low amplitude but fast, being alert Alpha quiet Theta quiet, sleep Delta super slow, deep sleep Diagnostic uses of EEG Epilepsy is associated with crazy EEGs Basically uncontrollable firing Spreads can lead to a seizure Evoked potentials Stimulus given Basically computer subtracts out the background EEG Used lots in research and in diagnostic areas Some disorders show characteristic ERPs Electrical Brain stimulation Basically put an electrode in the brain with the patient awake The classic Dr. Penfield approach Not nearly as effective as Penfield made it out to be… Looking at metabolism Blood flow techniques Use radioactive isotopes Look for anomalies SPECT sort of a poor mans…. PET scan Positron emission tomography MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI Basically a combo of RF signals and a REALLY strong magnetic field Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function Behavioural techniques These are really the kind of thing that involve say, touching your nose Or presenting a stimulus to one visual field and not the other Really quite telling, but nowadays you then end up in an MRI often Advances Basically the imaging techniques remain the same It is the computing power and software that is allowing for real time analysis that is having the biggest effect When MRI first came out the fastest desktop computer was MAYBE running a 75 MHz This little powerbook runs at 1.25 Ghz