* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Communication PowerPoint
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
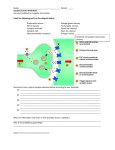
WHS AP Psychology Unit 3: Biological Psychology Essential Task 3-3: Describe the chemical process of transmitting a signal between neurons with specific reference to the synapse (synaptic vesicles, synaptic cleft and receptor sites), neurotransmitters (excitatory and inhibitory), drugs (agonists and antagonists) and reuptatke. Evolutionary Endocrine System We are here Building Blocks Biological Psychology Genetics Neurons Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Motor Brain Brain Imaging Spinal Cord Autonomic Sympathetic Neurotransmitters Sensory Somatic Parasympathetic Essential Task 3-3: Outline • Chemical communication between neurons – synapse • • • • Terminal buttons synaptic vesicles synaptic cleft receptor sites – neurotransmitters • Excitatory and inhibitory • Drugs (agonists and antagonists) • reuptatke Synapse Outline Synapse [SIN-aps] a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The synapse has 4 key components. Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. Terminal button - Enlarged area at the axon terminal Synaptic vesicles - Sacs in the terminal button that release chemicals called neurotransmitters into the synaptic space Synaptic space (synaptic cleft) - Tiny gap between neurons Receptor sites - Location on receptor neuron where neurotransmitters can bind. Chemical Communication Outline Terminal button Enlarged area at the axon terminal Synaptic vesicles Sacs in the terminal button that release chemicals called neurotransmitters into the synaptic space Synaptic space (synaptic cleft) - Tiny gap between neurons Receptor sites Location on receptor neuron where neurotransmitters can bind. Chemical Communication Outline Neurotransmitters Outline • Neurotransmitters (chemicals) released from the sending neuron that travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing it to generate an action potential. Neurotransmitters fit like chemical keys in chemical locks. Outline 2 Categories of neurotransmitters: Excitatory and Inhibitory Outline Excitatory •The key fits and ‘opens’ the receiving neuron. •Activation of the receptor causes depolarization of the membrane and promotes an action potential in the receiving neuron. Inhibitory •The key fits in but only stops any other keys. •Activation of the receptor causes hyperpolarization and depresses action potential generation. Drugs that excite a neuron are called Agonists Outline Agonist excites!!! Drugs that inhibit a neuron are called antagonists Outline Antagonists stops!!! Reuptake Outline • Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of reuptake. This process applies the brakes on neurotransmitter action. *Neurotransmitters are taken back Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Outline Citalopram (Celexa) Escitalopram (Lexapro) Fluoxetine (Prozac) Paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva) Sertraline (Zoloft)