* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
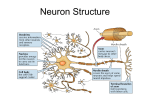
Tawsif Hossain Homeostasis Test (CNS) Multiple Choice 1) What is the resting membrane potential a) -70 mV b) -90 mV c) +40 mV d) 0 mV e) -70 V 2) The bipolar neuron has: a) Single main dendrite and axon b) Is found in the brain and spinal cord c) Has several dendrites and a single axon d) Has a single process that extends from the cell body e) Found in the peripheral nervous system. 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: a) Is used by the brain and autonomic neurons b) Acts as a natural painkiller c) Affects the brain synapses in the control of the body movements d) Regulates temperature and sensory perception e) None of the above 4) Which if the following option is false? In the sodium potassium pump a) No ATP is required b) 4 sodium ions are pumped outside the cell c) 1 potassium ions are pumped inside the cell d) channel proteins are required e) All of the above 5) Which of the following option is correct? The reflex arc: a) Involves the sensory,inter and motor neurons only b) Requires lot of time c) Involves voluntary control d) Composed of the central nervous system only e) More than one correct option Tawsif Hossain Fill in the blanks: An _________________ is the movement of an electrical impulse across the axon membrane as the nerve impulse occurs. The brief period in which the membrane cannot be stimulated to undergo another action potential is called _____________________. When the membrane potential becomes more negative than the original resting potential it becomes __________________. _________________ is a neurotransmitter that crosses a neuromuscular junction. ________________ are exposed areas of the axons of myelinated neurons. _________________ is the process of generating the resting potential. The central nervous system consists of the _______ and _________. The ______ of some neurons is coated by a layer called myelin sheath. Neurons are supported by another type of cells called __________. ______________ is involved in mood control. Long Answers: Q) Explain the action potential with a graph Q) A bacterial toxin breaks down the myelin sheath on the axons. Explain the potential consequences. Tawsif Hossain Homeostasis Test Solutions Multiple Choice 1) What is the resting membrane potential f) -70 mV Correct g) -90 mV Incorrect-(Hyperpolarized) h) +40 mV (Occurs when voltage gated channels are opened and sodium ions rush into the axon)- This occurs after the threshold potential and therefore cannot be the resting membrane potential. i) 0 mV-Incorrect, 0 States NO potential. j) -70 V-The value is too high. The value is in mV Millivolts not Volts 2) The bipolar neuron has: f) Single main dendrite and axon-Correct structure g) Is found in the brain and spinal cord-Incorrect it is found in the retina, inner ear and olfactory area of the brain. h) Has several dendrites and a single axon-Incorrect (Structure of Multipolar neuron) i) Has a single process that extends from the cell body-Structure of Unipolar neuron j) None of the above- Incorrect (Option f is correct) 3) Which of the option is true? Serotonin: f) Is used by the brain and autonomic neurons-Incorrect, it is norepinephrine. g) Acts as a natural painkiller-Incorrect, Endorphins h) Affects the brain synapses in the control of the body movementsIncorrect, Dopamine affects brain synapses i) Regulates temperature and sensory perception-Correct j) None of the above-Incorrect-Option iis correct. 4) Which if the following option is true? In the sodium potassium pump f) No ATP is required-Incorrect, it requires ATP g) 4 sodium ions are pumped outside the cell-Incorrect, 3 sodium ions. h) 1 potassium ions are pumped inside the cell-Incorrect, 2 Potassium ions i) channel proteins are required-Incorrect, carrier proteins are required. Tawsif Hossain j) All of the above are incorrect-Correct, none of the above are true. 5) Which of the following option is correct? The reflex arc: f) Involves the sensory, inter and motor neurons only- Correct g) Requires lot of time-Incorrect- Reflex arc is very fast h) Involves voluntary control-Incorrect, is involves involuntary control. i) Composed of the central nervous system only-Incorrect, involves the peripheral nervous system as well j) More than one correct option-Incorrect, only f is correct An action potential is the movement of an electrical impulse across the axon membrane as the nerve impulse occurs. The brief period in which the membrane cannot be stimulated to undergo another action potential is called refractory period When the membrane potential becomes more negative than the original resting potential it becomes hyperpolarized Acetlycholine is a neurotransmitter that crosses a neuromuscular junction. Nodes of Ranvier are exposed areas of the axons of myelinated neurons. Polarization is the process of generating the resting potential. The central nervous system consists of the Brain and Spinal Cord. The axon of some neurons is coated by a layer called myelin sheath. Neurons are supported by another type of cells called glial cells. Serotonin is involved in mood control. Long Answers: Tawsif Hossain A 1) Action potential is triggered by a stimulus. It is triggered when the threshold potential of approximately -50mV is reached. Once reached voltage gated sodium channels open and sodium ions move down the gradient into the axon. The potential difference of 40mV is reached. 2) As a result the sodium channels close and voltage gated potassium channels open. The potassium ions move down their concentration outside the axon carrying the positive charge out. This causes the membrane to become negative again. It becomes slightly more negative becoming hyperpolarized (-90mV) 3) The sodium potassium pump and diffusion bring the membrane back to the resting potential of -70mV. This is called repolarization. 4) For the next few ms the membrane cannot go through another action potential. This is called the refractory period. A 2)The myelin sheath is helps increase the speed at which impulses travel along the axon. Sometimes the body needs to take a very fast response such as in the case of the reflex arc. In the reflex arc a stimulus causes the body to react fast to prevent damage. For eg: if the sensory system detected a large rise in temperature of the skin surface. A nerve impulse would be sent through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and finally the motor neurons. It is critical that this information travels fast in order for the body to react appropriately. Tawsif Hossain Other very important functions such as thought processing and reaction time would be affected. This can reduce a person’s skill in areas where fast reaction times are critical such as driving. Other effects could include vision impairment and fatigue.