* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
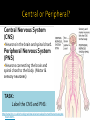
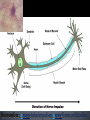
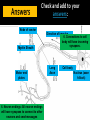
_N_E _ W __ _N RO _N_E _U R_ O_ N_ 6.5 Nerves Homework 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, motor end plates. 6.5.3 State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to the CNS by sensory neurons, within the CNS by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons. Outcome To understand how and why animals respond to their environment 1. Central nervous system 2. Peripheral nervous system 3. Stimulus 4. Receptor 5. Central nervous system 6. Motor neuron 7. Effector 8. Response What is it made of? Central Nervous System (CNS) Neurons in the brain and spinal chord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons connecting the brain and spinal chord to the body. (Motor & sensory neurones) TASK: Label the CNS and PNS: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/aqa/human/thenervoussyste mact.shtml - Key Facts When neurons are stimulated they send rapid electric impulses. Super fast messages. Gaps between neurones: synapses Impulses travel from one neuron to another across synapses . There are hundreds of types! Remember: axons take impulses away from cell bodies. LO1: Describe the structure of neurons LO2: Relate the structure of neurons to their function Task Annotate the diagram: link STRUCTURE to FUNCTION. Long axon (cytoplasm extension) to send electrical impulses from central nervous system to motor neuron. 2. Myelin sheath insulates the axon, speeding-up transmission of electrical impulses. 3. Arrow to show the direction of the nerve impulse. 4. Node of ranvier, a periodic gap in the myelin sheath 5. Cell body/nucleus (axon hillock) which integrates signals 6. Motor end plate which transmit impulses across synapses to other neurons 1. EXT Label one place at either end of the neuron where you would expect to find a synapse (gap between two neurons which communicate) Check and add to your answers: Node of ranvier Myelin Sheath Motor end plates 6. Neuron endings: All neuron endings will have synapses to connect to other neurons and send messages Direction of impulse 6. Connections to cell body will have incoming synapses. Long Axon Cell body Nucleus (axon hillock) Smell Touch Pressure and temperature Sight Light Tongue Taste Hearing Sound and Balance Collect info and send it to sensory neurons Receptors can be part of organs, like the eye. Stimulus: Loud Sound Neurons : SRM Receptor: Sensory neuron in ear Relay neuron: Brain/Spinal chord (CNS) Effector: Motor Neuron/Gland Response: Jump https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OdOOIxcUjAs Label the diagram to show how he responds and survives, including PNS, CNS and names of each parts of the circuit Car comes towards Relay man in daylight in PNS CNS PNS 1. What two things make up the central nervous system? Brain and spinal chord 2. What is a receptor? Explain and give an example. Something that receives information. Receptors in the ear receive sound. 3. What is an effector? Explain and give an example. Something that causes a response. Receives message from motor neurone and causes muscle/gland response. 4. Why do animals need to respond to stimulus? To survive / Avoid horrible painful deaths. Ext: Give an example of an animal responding to a stimulus: give examples of stimulus, receptor, CNS, effector and response. (Draw a flow map if its easier) HeatTemperature receptor in skin relay neurone in CNS Effector = Muscle Response = Movement away from heat Stimulus – bright light in eyes Stimulus Receptor Sensory Neuron Relay Neuron Motor Neuron Effector Response Response – raise hand to shield eyes