* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The human brain
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
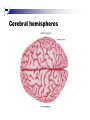
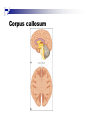
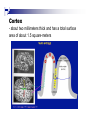
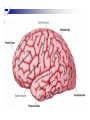
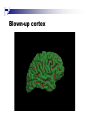
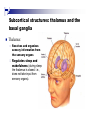
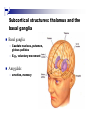
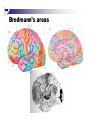
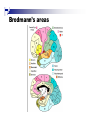
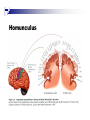
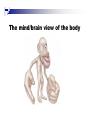
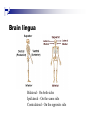
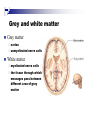
The human brain An extension of the spinal cord which has become bigger and bigger as the species has evolved. Cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum Cerebrum (Latin: "brain”): Largest part of the brain. Cerebellum (Latin: "little brain"): Coordination and control of voluntary movement Brain stem: breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure Gross generalizations about function Frontal lobe: Temporal lobe: perception, recognition, many aspects of language Parietal lobe: decisions, judgments, problem solving, emotions. movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital lobe: vision at large Cortex - about two millimeters thick and has a total surface area of about 1.5 square-meters Blown-up cortex Subcortical structures: thalamus and the basal ganglia Thalamus: Receives and organizes sensory information from the sensory organs Regulates sleep and wakefulness (during sleep the thalamus is closed. i.e., does not take input from sensory organs). Subcortical structures: thalamus and the basal ganglia Basal ganglia: Caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus E.g., voluntary movement Amygdala: emotion, memory Cortical layers Cytoarchitectonics: the arrangement of nerve cells in the cerebral cortex Korbinian Brodmann, (1868 - 1918) Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. Brodmann’s areas Brodmann’s areas Homunculus The mind/brain view of the body Brain lingua Brain lingua Brain lingua Bilateral - On both sides Ipsilateral - On the same side Contralateral - On the opposite side Neurons Central nervous system is made up of about 100 billion neurons. Unlike other cells in that they can both receive and send out signals to neighboring neurons in the form of electrical pulses. Neurons Typically a given neuron is connected to about ten thousand other neurons. The specific point of contact between the axon of one cell and a dendrite of another is called a synapse. Neurons We are born with a complete set of neurons. What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. Neurons http://www.dnatube.com/video/1107/Neurons-and-How-They-Work Grey and white matter Grey matter cortex unmyelinated nerve cells White matter myelinated nerve cells the tissue through which messages pass between different area of grey matter How fast is the brain? After a neuron has fired, it takes it about one millisecond to return to its normal state. Much slower than your computer! The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected.