* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous Systems
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
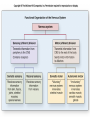
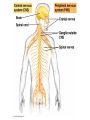
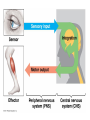
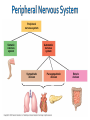
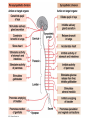
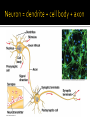
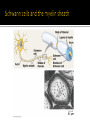
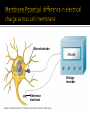
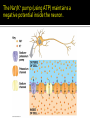
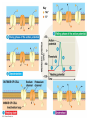
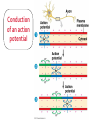
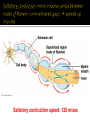
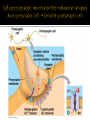
Chapters 48 Campbell Biology – 9th ed. The anatomy of a neuron. The mechanisms of impulse transmission in a neuron. The process that leads to release of neurotransmitters, and what happens at the synapse. Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons Contains motor neurons +/or sensory neurons Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Enteric division cell body: contains nucleus & organelles dendrites: receive incoming messages axons: transmit messages away to other cells myelin sheath: fatty insulation covering axon, speeds up nerve impulses synapse: junction between 2 neurons neurotransmitter: chemical messengers sent across synapse Glia: cells that support neurons Eg. Schwann cells (forms myelin sheath) Microelectrode –70 mV Voltage recorder Reference electrode The Na+/K+ pump (using ATP) maintains a negative potential inside the neuron. Resting potential: membrane potential at rest; polarized Na+ outside, K+ inside cell Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes All-or-nothing response Na+ channels open Na+ enters cell K+ channels open K+ leaves cell Conduction of an action potential Saltatory conduction speed: 120 m/sec Chemicals released from vesicles by exocytosis into synaptic cleft Diffuse across synapse Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells Types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane Acetylcholine (ACh): stimulates muscles, memory formation, learning Epinephrine: (adrenaline) fight-or-flight Norepinephrine: fight-or-flight Dopamine: reward, pleasure (“high”) Loss of dopamine Parkinson’s Disease Serotonin: well-being, happiness Low levels Depression GABA: inhibitory NT Affected by alcohol LSD/mescaline – bind to serotonin and dopamine receptors hallucinations Prozac – enhances effect of serotonin by inhibiting uptake after release Morphine, heroin – bind to endorphin receptors decrease pain perception Viagra – increase NO (nitric oxide) effects maintain erection Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) – develop senile plaques, shrinkage of brain tissue Poster Presentation: Drug: Neurotransmitter(s) Involved Action of Drug: Summary Illustration