* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 大腦神經解剖與建置
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
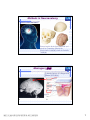
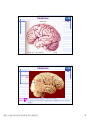
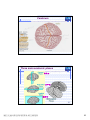
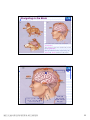
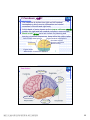
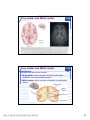
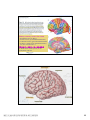
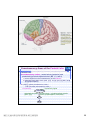
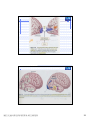
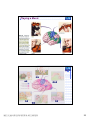
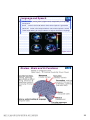
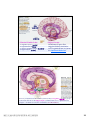
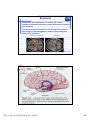
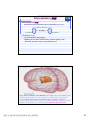
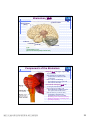
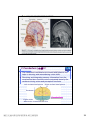
普通生物學 -神經系統與應用 Chapter 49 神經系統 Nervous System (中樞神經系統CNS) 柯立偉 老師 交通大學生物科技學系 Outline Nervous System 神經系統 (review) Organization of Vertebrate Nervous System Five Different Neurons in Nervous System Glia Cell in the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy and Development (大腦神經解剖與建置) Brain and Spinal Cord Overview (大腦,小腦,間腦,腦幹) 大腦 間腦 腦幹 小腦 脊隨 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 1 ※ Organization of Vertebrate Nervous System※ In vertebrates The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and Central nervous Peripheral nervous system (CNS) system (PNS) ganglia. Brain Spinal cord Cranial nerves Ganglia outside CNS Spinal nerves Figure 49.4 Organization of Vertebrate Nervous System The spinal cord conveys information from and to the brain and also produces reflexes independently of the brain A reflex 反射動作 is the body's automatic response to a stimulus For example, a doctor uses a mallet to trigger a kneeCell body of Gray jerk reflex sensory neuron in Quadriceps muscle matter dorsal root ganglion White matter Hamstring muscle Spinal cord (cross section) Figure 49.3 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 Sensory neuron Motor neuron Interneuron 2 ※ Different Neurons in Nervous System※ ※ Glia in the Nervous System※ CNS VENTRICLE Cilia PNS Neuron Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell Microglial Capillary Figure 49.6 Glia have numerous functions to nourish 滋養, support, and regulate neurons. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 3 Glia in the Nervous System Astrocyte (星形膠質細胞) It induce cells lining capillaries in the CNS to form tight junctions, resulting in a blood-brain barrier and restricting the entry of most substances into the brain. Microglia (小膠質細胞) Immune cells that protect against pathogen 病原體. Oligodendrocyte (少突膠質細胞) Generating myelinate 髓鞘 axon in the CNS, greatly increases the conduction speed of action potentials. Schwann cell Generating myelinate髓鞘 axons in the PNS. Central Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy and Development 大腦神經解剖與建置 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 4 Motivation The relationship between brain anatomy (解剖學) and cognition has been the source of fascination (魅力) and puzzlement (迷惑) for hundreds of years. 舉例來說,許多研究認為大腦組織功能與智慧是有關聯的。 ex. Albert Einstein To identify unique anatomical features of Einstein’s brain that might explain his genius. When he died in 1955 at the age of 76, his brain was extracted and saved. weighed, perfused with formalin, measured and photographed sectioned and embedded in a material that permitted it to be thinly sliced to make histological slides for microscopic analysis To compare with the brains from a few dozen normal persons that had been donated for scientific research. IQ vs. Brain Organization 我的腦哪裡不一 樣?? 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 5 Two Prominent Features of Einstein’s Brain First: the Sylvian fissure (大腦側裂溝) (the division that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes), in Einstein’s brain had an unusual anatomical organization. Unlike the control brains, Einstein’s brain showed a strange confluence (匯集處) of the Sylvian fissure with the central sulcus on the brain’s lateral surface. The Sylvian fissure in most brains projects posteriorly (後面) to end in an area surrounded by the supramarginal gyrus (腦回邊界之上). Second: Einstein’s inferior parietal lobe (下頂葉) was actually larger, and indeed thicker (較厚的) in lateral to medial extent. The increased size of Einstein’s inferior parietal cortex might have been related to his intellectual capacity. (Hypothesis, not conclusion) From such investigations, hypotheses can be generated and then tested in brains removed at autopsy or, in the modern age of neuroimaging, in brains in the living human. Neuroanatomy the branch of anatomy that studies the anatomical organization of the nervous system • Gross neuroanatomy : the focused is on general structures and connections visible to the naked eyes (裸眼) • Microscopic neuroanatomy (fine neuroanatomy) : to describe the organization of neurons and their connections and subcellular structure 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 6 Methods in Neuroanatomy How to view the brain? ? Removing the brain from the head and put it in a container filled with preservative (防腐劑) such as formalin (福馬林) Meninges (腦膜) a dense layers of collagenous fibers (膠原纖維) 硬腦膜 蛛網膜 軟腦脊膜 動脈 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 7 Meninges Both the brain and spinal cord are protected by a tough protective tissue called meninges consisting of three layers: • Dura matter • Arachnoid membrane • Pia matter 15 The photograph of the human brain Cerebrum Brain stem cerebellum Spinal cord 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 8 Cerebrum Cerebrum gyrus (gyri) sulcus (sulci) Gyri (腦回): the protruding (突出) rounded surface Sulci (溝): the numerous smaller invaginations (堆疊) seen as creases (皺摺) 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 9 Cerebrum Three main anatomic planes 冠狀切 水平切 箭狀切 20 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 10 Navigating in the Brain • The front is the rostral end, toward the frontal lobes. • The posterior end is the caudal end, toward the occipital lobe. • The top and bottom are, respectively, the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the brain. 1.5kg average 腦 gyrus (gyri複):凸處迴轉 sulcus (sulci複):皺褶 ventricular:腦室 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 20%氧在腦 缺氧10分即死 身體動/不動腦中 血液變化小 11 Different View of the Brain dorsal view ( horizontal axial section) front 右 左 lateral view (sagittal section) dorsal Interhemispheric fissure (longitudinal fissure) frontal occipital occipital ventral sylvian fissure(裂溝) →區分temporal lobe from frontal lobe 及parietal Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 12 Human Brain Development Brain structures in child and adult Embryonic brain regions Cerebrum (includes cerebral cortex, white matter, basal nuclei) Diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus) Telencephalon Forebrain Diencephalon Midbrain Mesencephalon Midbrain (part of brainstem) Metencephalon Pons (part of brainstem), cerebellum Myelencephalon Medulla oblongata (part of brainstem) Hindbrain Midbrain Hindbrain Diencephalon Cerebrum Mesencephalon Metencephalon Diencephalon Myelencephalon Forebrain Telencephalon Embryo at 1 month Embryo at 5 weeks Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Spinal cord Spinal cord Figure 49.9b Child ※ Overview of Our Brain※ Left cerebral hemisphere Right cerebral hemisphere Cerebrum 大腦 Cerebral cortex 大腦皮層 Corpus callosum 胼胝體 Basal nuclei 基底核 Figure 49.9d Cerebellum 小腦 Figure 49.9c 間腦 Diencephalon 視丘 Thalamus 松果體 Pineal gland 下視丘 Hypothalamus 腦下垂體 Pituitary gland 腦幹 Brainstem Spinal cord 脊髓 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 Midbrain Pons 橋腦 Medulla oblongata 延腦 13 ※ Cerebrum 大腦※ The cerebrum is divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres, which receive information and control movement of the left and right body. A thick band of axons known as the corpus callosum 胼胝體 enables the right and left cerebral cortices to communicate. Basal nuclei 基底核 serve as centers for planning and learning movement sequences, deep within the white matter. Left cerebral hemisphere Right cerebral hemisphere Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Basal nuclei Figure 49.9c Adult brain viewed from the rear Four Lobes: sylvian sulcus 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 14 Gray matter and White matter Gray matter and White matter The brain and spinal cord contain Gray matter, which consists of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons White matter, which consists of bundles of myelinated axons Gray matter White matter Ventricles Figure 49.5 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 15 Primary sensory cortex for vision • • • • Brodmann area 17, BA 17 Striate cortex (cytoarchitectonic name) Calcarine cortex (gross anatomical name) Primary visual cortex (functional name), V1 (for “visual area 1”) 不同命名不一定都有一對一的對應區域 Ex. BA18 of the visual system, is not synonymous with V2. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 16 Functions of Human Cerebral Cortex Figure 49.15 Frontal lobe Motor cortex (control of skeletal muscles) Somatosensory cortex (sense of touch) Parietal lobe Prefrontal cortex (decision making, planning) Sensory association cortex (integration of sensory information) Visual association cortex (combining images and object recognition) Broca’s area (forming speech) Temporal lobe Occipital lobe Auditory cortex (hearing) Wernicke’s area (comprehending language) Cerebellum Visual cortex (processing visual stimuli and pattern recognition) Motor Areas of the Frontal Lobe Frontal lobe: planning / execution of movements a. motor cortex : precentral gyrus =Motor strip primary motor cortex (M1): BA4 b. prefrontal cortex a* precentral gyrus:primary motor cortex之前有2個more main motor areas (within BA6). premotor cortex (lateral surface) supplementary motor cortex (dorsal to premotor area) * Axons in motor neurons extend to the spinal cord and brainstem * Synapse on motor neurons in the spinal cord 2部分 b. prefrontal cortex (high-order association areas): higher aspects of motor control planning / execution of behaviors that require the integration of information over time分3 more areas: 1.dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex → working memory 2.orbitofrontal cortex 3.anterior cingulate and medial front regions 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 17 Somatosensory Areas of the Parietal Lobe Parietal Lobe somatosensory cortex : central sulcus (posterior) and postcentral gyrus and adjacent areas. (BA 1, 2, and 3) 1.receive inputs from the somatosensory of the thalamus 2.represent information: touch, pain, 溫度, 四肢姿態的信息(limb), 本體 感受(proprioception) 分為SⅠ (primary somatosensory cortex ) SⅡ (secondary somatosensory cortex ) Two pathways: 外界sensory signal Thalamus anterolateral system (pain, 溫度) dorsal column – medial lemniscal system (touch, proprioception, movement) SⅠ SⅡ 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 18 Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Jaw Tongue Leg Hip Trunk Neck Head Knee Hip Genitalia Toes Tongue Pharynx Primary motor cortex Abdominal organs Primary somatosensory cortex Figure 49.17 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 19 Direct Stimulation on the Cortex Visual Processing Areas in the Occipital Lobe Retina Thalamus Lateral geniculate nucleus V1: primary visual cortex (≡striate cortex) 埋在occipital lobe的 (Bradmann Area 17) calcarine fissure中 Colors/亮度/空間 primary visual pathway cortical projector (retina頻率/orientation geniculo-striate pathway) /movement (Details in Ch5 & 6) subcortical brain region Retina superior colliculus of midbrain visuomotor functions (如眼動, eyemovents) secondary(2nd)visual pathway (subcortical projection) 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 20 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 21 Auditory Processing Areas in the Temporal Lobe and Association Cortex Temporal Lobe (TL) BA 22 (surrounds the auditory cortex) Primary Auditory cortex: aids in the perception of auditory inputs (1) superior part of Temporal Lobe (BA 41 & 42) (2) buried (埋) in sylvian (lateral) fissure (tonotopic organization) cochlea 耳蝸 subcortical relay medial geniculate of thalamus supratemporal cortex (Heschl’s gyri) Association Cortex Cortex 中非sensory / motor區(Audio/video/ somatosensory等), 皆為association cortex ,如 front cortex / temporal cortex Ex:(1)visual association cortex (在parietal及temporal lobes) (2)parietal-temporal-occipital junction 在左腦:language processing 在右腦:attentional orienting 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 22 Playing a Music 動覺 味覺 體感覺 嗅覺 視覺 聽覺 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 23 Language and Speech Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech Broca's area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated Wernicke's area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard These areas belong to a larger network of regions involved in language Max Hearing words Seeing words Speaking words Generating words Min Figure 49.16 Review - Brain and its Functions 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 24 新皮質 細皮質 基底核 間腦 Cingulate gyrus 扣帶迴 Hippocampus 海馬迴 (allocortex) Limbic lobe 邊緣葉(系統) Limbic Lobe (邊緣葉) Limbic Lobe mesocortex → 6層 (如cingulate gyrus) allocortex → 1~4層 (如hippocampus) temporal / frontal /parietal / occipital lobes≡6層neocortex (新皮質) • 人類的新皮質 (neocortex)佔整個腦 的76%。 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 25 穹窿 (拱型空間) 前聯合喉 • Classical Limbic Lobe: 1. cingulate Gyrus (扣帶迴) 2. hypothalamus (下視丘) 3. anterior thalamic nuclei (前丘腦核) 4. hippocampus (海馬迴) • Papez Circuit: 1930 James Papez first suggested these structures were organized into a system for emotional behavior. • Two key components of the Limbic system (today): amygdala (杏仁核), a group of neurons anterior to the hippocampus (orbitofrontal cortex + parts of basal ganglia + medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus, not shown here). 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 26 Limbic Lobe Hippocampus(海馬迴) -inferior and media of temporal lobe -分為4 CA (cornu ammonis 大角) fields CA1~CA4 dentate gyrus Entorhinal cortex 嗅皮質 cingulate cortex pyramidal nervous hippocampus fornix 與memory 及emotional processing(由於hippocampus與 cingulate mammillary bodies 與limbic system互連 ) papez circuit → emotional behavior Amygdala(核心)+orbitofrontal cortex+(parts of) basal ganglia +medial dorsal nucleus of thalamus Limbic Lobe :演化史上neo cortex老原始 與emotional processing, learning, and memory 有關 Emotions Generation and experience of emotions involve many brain structures including the amygdala 杏仁核, hippocampus 海馬迴, and parts of the thalamus視丘, are grouped as the limbic system . The limbic system also functions in motivation, olfaction, behavior, and memory. Thalamus Hypothalamus Olfactory bulb Figure 49.13 Amygdala 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 Hippocampus 27 Emotions Generation and experience of emotion also require interaction between the limbic system and sensory areas of the cerebrum. The structure most important to the storage of emotion in the memory is the amygdala, a mass of nuclei near the base of the cerebrum. Nucleus accumbens Happy music 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 Amygdala Sad music Figure 49.14 28 Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (腦部基底核) -subcortical structures (在側腦室 (lateral ventricles)之前) -在control of movement 扮演重要的角色 -細分成3部分:(Fig 3.20, p80) globus pallidus (蒼白球) corpus caudate nucleus (尾狀核) striatum Putamen (硬核) neostriatum basal ganglia + subthalamic nucleus + substantia nigra ≡ (i) motor control [somatic motor and oculomotorsystems] (ii) cognitive functions : short-term memory process (dorsolaternal prefrontal cortex) execution functions (behaviors) • The subthalamic nucleus (丘腦 底部) and the substantia nigra (黑質) are considered part of the basal ganglia. • Parkinson與位於中腦(midbrain) 的substantia nigra有密切關係, 因substantia nigra中生產 dopamine的細胞大量死亡所致。 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 29 ※ Diencephalon (間腦)※ Diencephalon Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Figure 49.9d Diencephalon (間腦) Incoming information from all the senses is sorted in the thalamus 視丘 and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary hormones and of releasing hormones that act on the anterior pituitary. The epithalamus includes the pineal gland 松果體 the source of melatonin. Diencephalon Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Spinal cord 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 Figure 49.9d 30 Diencephalon (間腦) Diencephalon (間腦) 含thalamus (inner chamber含意) 及hypothalamus (下視丘) Massa intermedia 左右連接 左thalamus 右thalamus Thalamus (視丘) 座落於brainstem 最前端(蛋形) gateway to the cortex for the sensory systems (雙間)亦參與 brainstem projection system (嗅覺olfactory除外) • Fig. 3.24 Gross anatomy of the thalamus. This diagram shows the thalamus of the left and right hemispheres in a see-through brain. The thalamus is egg shaped. It serves as the gateway to the cortex for the sensory systems and contains reciprocal loops with all cortical regions, organized according to subdivisions of the thalamus. The thalamus also is innervated by brainstem projection systems. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 31 ※ Brainstem (腦幹)※ Brainstem Midbrain Pons 橋腦 Medulla oblongata 延腦 Figure 49.9d Brainstem (腦幹) The brainstem consist of the midbrain, the pons 橋腦 and the medulla oblongata 延腦. The midbrain coordinates visual reflexes, such as the peripheral vision reflex. A major function of the pons and medulla is to transfer information between the PNS and the midbrain and forebrain, also helping coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running and climbing. An additional function of the medulla is the control of several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breath, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing 吞嚥, vomiting 嘔吐, and digestion 消化. Brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Figure 49.9d Spinal cord 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 32 Brainstem (腦幹) cerebral cortex Diencephalon (間腦) midbrain hindbrain pons medulla spinal cord 控制: (1)respiration(呼吸) (2)consciousness (sleep/ wakeness) Components of the Brainstem The pons 橋腦: the upper segment of the brain stem It contains nerve fibers that connect the two halves of the cerebellum. It is vital in coordinating movements involving right and left sides of the body. The medulla oblongata 延腦: the lower part of brain stem It transmits ascending and descending nerve fibers between the spinal cord and the brain. It also directly controls many involuntary muscular and glandular activities, including breathing, heart contraction, artery dilation, salivation, vomiting, and probably laughing. 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 33 ※ Cerebellum (小腦)※ The cerebullem coordinates movement and balance and helps in learning and remembering motor skills. Receiving and integrating sensory information from the muscles and also monitors motor commands issue by the cerebrum during motor and perceptual functions. Left cerebral hemisphere Right cerebral hemisphere Cerebrum Cerebellum Figure 49.9c Adult brain viewed from the rear 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 34 Cerebellum (小腦) Cerebellum(小腦)包括: (1)cerebellum cortex (2)4對deep nuclei (3)internal white matter =I/O 功能: 維持posture (姿態), walking, coordinated movement 小腦不直接控制movements而整合body & motor commands 去modify motor flow 產生smooth而協調的行為動作. Process of Movement Inputs (1)brain中處理 motor/sensory資料 (描述body position) (2)vestibular projection(平衡) (3)audiory/visual inputs spinal cord 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 cerebellum I/P Deep nuclei O/P Thalamus I/P brainstem brainstem nucleus motor premotor cortex 35 ※ Spinal Cord (脊椎神經)※ 在medulla到末梢神經(全身)之間 Ventral root →傳遞final motor signal 到muscles Dorsal root →傳遞peripheral sensory info到brain Ventral Horn: contains the large motor neurons that project to muscles Dorsal Horn: contains sensory neurons and interneurons. at each level of spinal cord 存在reflex pathway (如knee-jerk reflex) 國立交通大學生物科技學系 柯立偉老師 36