* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Notes
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
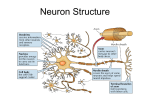
Psy 113 / Malone Ch. 2 1 Chapter 2 Brain and Behavior Neuron and Its Parts • Neuron: Individual nerve cell – Dendrites: – Soma: cell body; body of the neuron – Axon: – Axon Terminals: Branches that link the dendrites and somas of other neurons The Nerve Impulse • Resting Potential: Electrical charge of an inactive neuron • Threshold: • Action Potential: A nerve impulse; Primarily an electrical process; Gates or channels in the axon membrane pop open, allowing sodium ions to rush into the axon; This process continues along the length of the axon. Synapses – Synapse: Microscopic gap between two neurons over which messages pass; this communication at the synapse is a chemical process Neurotransmitters • Chemicals that alter activity in neurons; brain chemicals – Acetylcholine: – Dopamine: – Serotonin: • Receptor Site: Areas on the surface of neurons and other cells that are sensitive to neurotransmitters Psy 113 / Malone Ch. 2 2 Nerves and Neurons • Nerves: Large bundles of axons and dendrites • Myelin: Fatty layer of tissue that coats axons – Multiple Sclerosis (MS) occurs when myelin layer is destroyed; numbness, weakness, and paralysis occur Subparts of the Nervous System • Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System: All parts of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord – Somatic System: Links spinal cord with body and sense organs; controls voluntary behavior – Autonomic System: Serves internal organs and glands; controls automatic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure Two Divisions of the Autonomic System • Sympathetic: Arouses body; emergency system • Parasympathetic: Quiets body; most active after an emotional event SKIP Research Methods (bottom p. 69- 72) Cerebral Cortex Definition: Outer layer of the cerebrum (Cerebrum: Two large hemispheres that cover upper part of the brain) Corticalization: Increase in size and wrinkling of the cortex Cerebral Hemispheres: Right and left halves of the cortex Corpus Callosum: Bundle of fibers connecting cerebral hemispheres Hemispheric specialization: Some cortical functions are localized to a particular hemisphere of the brain . In general, the left hemisphere specializes in: In general, the right hemisphere specializes in: Psy 113 / Malone Ch. 2 3 Split Brains • Corpus Callosum is cut; done to control severe epilepsy (seizure disorder). • Result: Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex • • • • • • As discussed, the cerebral cortex can be divided into two hemispheres We can further divide the cortex into several smaller area called lobes Occipital: Back of brain; vision center Parietal: Just above occipital; bodily sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature Temporal: Each side of the brain; auditory and language centers Frontal: Movement, sense of smell, higher mental functions – Contains motor cortex; controls motor movement Association Areas • Association Cortex: Combine and process information from the five senses • Aphasia: Speech disturbance resulting from brain damage • Broca’s Area: Related to language and speech production • Wernicke’s Area: Related to language comprehension Divisions of the Subcortex Hindbrain or Brainstem • • The brainstem consists mainly of medulla and cerebellum Medulla: Connects brain with the spinal cord. Controls vital life functions—heart rate, breathing, swallowing, etc. • Cerebellum: located at base of brain and looks like a miniature cerebral cortex; regulates posture, muscle tone, and muscle coordination; stores memories related to skil ls and habits • Pons: bridge between medulla and other brain areas; also influences sleep and arousal Psy 113 / Malone Ch. 2 4 Reticular Formation (RF) • Lies inside medulla and brainstem Associated with alertness, attention and some reflexes (breathing, coughing, sneezing, vomiting) • Reticular Activating System (RAS): Part of RF that keeps the cortex active and alert • Its alarm clock Midbrain • Link between the forebrain and the brainstem Forebrain • Structures are part of Limbic System: System within forebrain closely linked to emotional response Thalamus: final switching station for sensory messages on their way to the cortex Hypothalamus: control center for emotion and many basic motives (e.g., sex, eating, drinking, sleep) Amygdala: provides a quick pathway to the cortex for fear messages Hippocampus: vital in forming lasting memories (SKIP The Endocrine System & Handedness p. 84-86)