* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4. Nervous System: Synapses
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
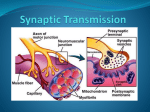
Synapses Synapse • Location where information is transmitted from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron- gap where axon terminal meets dendrite of next neuron • Neurotransmitter molecules released into this space • Synapses can be electrical or chemical • Electrical synapse: electrical current flows between 2 cells – Via Gap Junction – Cell membranes are continuous – in cardiac muscle and some smooth muscle cells • Chemical synapse – Neurotransmitters: chemicals that move from one cell to the next to carry the signal across a space to the next cell • Examples: acetylcholine serotonin norepinephrine histamine dopamine 3 parts of synapse: • 1. synaptic knob—bulge at end of one axon terminal of presynaptic neuron • 2. synaptic cleft-tiny (25 nm) gap between two neurons • 3. plasma membrane of post synaptic neuron– usually at the dendrite or cell body- contains protein receptors Synaptic transmission • Action potential itself cannot cross cleft • Instead neurotransmitters released from knob, attach to receptors in next neuron, and cause response in next neuron Neurotransmitters • Two categories: – Excitatory: cause depolarization in postsynaptic neuron (stimulate next neuron) – Inhibitory: cause hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane that inhibits/stops the potential from moving on • Drugs can be inhibitory or excitatory • Endorphins are inhibitory- block pain Neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters cause ion channels to open – Some channels let Na+ ions in depolarization – Other channels let K+ ions out and Cl- in hyperpolarization that inhibits action potential Summation • Summation: amount released by one knob won’t start AP in next neuron—may need several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? Summation… • Much sensory information gets stopped at synapses where threshold was not reached • Summation= mechanism for making decisions about what info is important to move on Synapses and Memory • Theory: info is stored in form of increased flow of info at synapses in particular pathways • Certain neurotransmitters and structural changes in synapses may affect short vs. intermediate vs. long term memories • Ex: more synapses and receptors are built when we create long term memories