* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sensory neurons
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
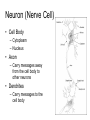
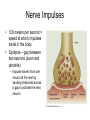
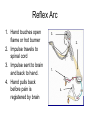
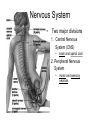
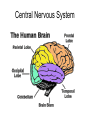
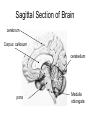
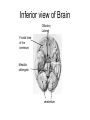
Neuron (Nerve Cell) • Cell Body – Cytoplasm – Nucleus • Axon – Carry messages away from the cell body to other neurons • Dendrites – Carry messages to the cell body Types of Neurons Receptor Cells Receives information from a stimulus • • Sensory Neurons – Carry the impulse to the spinal cord • • Travels the length of the arm to the spinal cord Interneurons – Impulse is transmitted to the brain and the motor neurons via synapses • • For example - your finger gets hit by a hammer Travels to the brain to register pain and out to the finger Motor neurons – Sends the processed information back to finger • Carries impulse to the effector cells in the fingers, hand and arm Nerve Impulses • 120 meters per second = speed at which impulses travel in the body. • Synapse – gap between two neurons (axon and dendrite) – Impulse travels from one neuron to the next by sending chemicals across a gap to activate the next neuron. Reflex Arc 1. Hand touches open flame or hot burner 2. Impulse travels to spinal cord 3. Impulse sent to brain and back to hand. 4. Hand pulls back before pain is registered by brain 3. 2. 1. 4. Nervous System • Two major divisions 1. Central Nervous System (CNS) • brain and spinal cord 2. Peripheral Nervous System • motor and sensory neurons Central Nervous System Development of the brain Conception - newborn Sagittal Section of Brain cerebrum Corpus callosum cerebellum pons Medulla oblongata Inferior view of Brain Olfactory Lobes Frontal lobe of the cerebrum Medulla oblongata cerebellum Regions of the Brain • Cerebrum - thought and reasoning – – – – • • • • Frontal - thinking, talking, remembering, moving Parietal - touching Occipital - seeing Temporal – tasting, smelling, hearing Cerebellum – coordination of muscular movements Medulla Oblongata – involuntary responses Pons – band of nerves linking the medulla and the cerebellum Olfactory – sense of smell Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System • Consist of the neurons (receptor and motor) which lead to and from the central nervous system • Two divisions – Sensory Somatic – Autonomic