* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 凌树才_边缘系统
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Adult neurogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Inferior temporal gyrus wikipedia , lookup
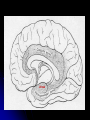
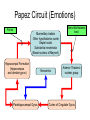
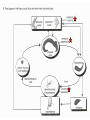
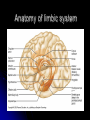
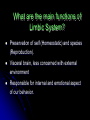
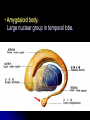
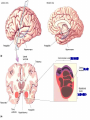
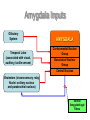
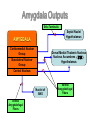
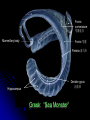
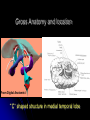
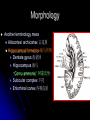
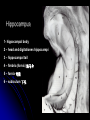
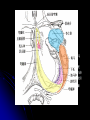
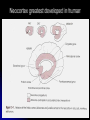
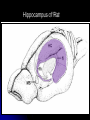
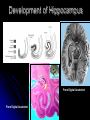
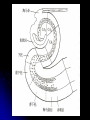
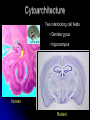
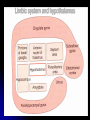
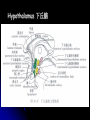
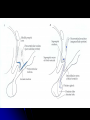
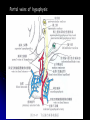
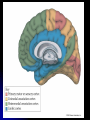
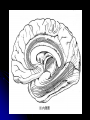
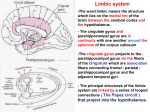
Central Nervous System Limbic System 边缘系统 Introduction History Paul Broca (1824-1880): a French physician, surgeon,anatomist, and anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. Uncus James Papez (1883-1958): an American neuroanatomist He is most famous for his 1937 description of the Papez circuit which is a neural pathway in the brain thought to be involved in the cortical control of emotion. Papez Circuit (Emotions) Fornix Mammillary bodies Other hypothalamic nuclei Septal nuclei Substantia innominata (Basal nucleus of Meynert) Hippocampal Formation (hippocampus and dentate gyrus) Parahippocampal Gyrus Neocortex Mammillothalamic tract Anterior Thalamic nuclear group Cortex of Cingulate Gyrus Paul D. MacLean (1913-2007) an American physician and neuroscientist who made significant contributions in the fields of physiology, psychiatry, and brain research. The term ‘limbic system’ was first used by MacLean in 1952 to describe a set of structurally and functionally related structures of the brain bordering the midline, inner surface of each cerebral hemisphere. The main circuit of Limbic System Anatomy of limbic system What are the components of limbic system ? Core component: hippocampus and amygdala. Cortex: Cingulated and prefrontal cortex. Nuclei: hippocampus , septal , amygdala. Anterior and dorsomedial thalamus Hypothalamus- mammillary body and ventromedial hypothalamus. What are the main functions of Limbic System? Preservation of self (Homeostatic) and species (Reproduction). Visceral brain, less concerned with external environment Responsible for internal and emotional aspect of our behavior. What are the other important functions of limbic System? Generates emotions (Emotional brain) Add feeling to sensory experience which direct to behavior. Affect: interpret the sensory experience as pleasant or unpleasant. Memory and learning which is closely linked to emotion. Sexual behavior, emotions of rage ,fear, anxiety and motivation Components Amygdaloid body 杏仁体 Hippocampus (“seahorse”) 海马 Hypothalamus 下丘脑 Parahippocampal gyrus 海马旁回 Cingulate gyus 扣带回 Mamillary bodies 乳头体 Anterior nucleus of thalamus 丘脑前核 Part 1. Amygdaloid body • Amygdaloid body : Large nuclear group in temporal lobe. Regions of the Amygdala Large basolateral region: 基底外侧核 Provides direct input to basal ganglia and motor system. Small corticomedial group of nuclei: 皮质内侧核 Related to olfactory cortex. Central nuclei: 中央核 Connected to hypothalamus. (皮质内侧核) (中央核) (基底外侧核) Amygdala Connections Cerebral cortex(大脑皮质) Olfactory system(嗅觉系统) Thalamus(丘脑) Brainstem reticular formation (脑干网状结构) Stria Terminalis 终纹 Hypothalamus 下丘脑 AMYGDALA Ventral Amygdalofugal fibers 杏仁核腹侧通路 Amygdala Inputs Olfactory System Temporal Lobe (associated with visual, auditory, tactile senses) AMYGDALA Corticomedial Nuclear Group Basolateral Nuclear Group Central Nucleus Brainstem (viscerosensory relay Nuclei: solitary nucleus and parabrachial nucleus) Ventral Amygdalofugal Fibers Amygdala Outputs Stria Terminalis Septal Nuclei Hypothalamus AMYGDALA Corticomedial Nuclear Group Dorsal Medial Thalamic Nucleus Nucleus Accumbens(伏核) Hypothalamus Basolateral Nuclear Group Central Nucleus Nuclei of ANS Ventral Amygdalofugal Fibers Ventral Amygdalofugal Fibers Functions of the Amygdala Relate environmental stimuli to coordinated behavioral autonomic and endocrine responses seen in speciespreservation. Responses include: Feeding and drinking Agnostic (fighting) behavior Mating and maternal care Responses to physical or emotional stresses. Part 2. Hippocampus Fornix commissure 穹窿连合 Mammillary body Fornix 穹窿 Fimbria 海马伞 Dentate gyrus 齿状回 Hippocampus Greek: “Sea Monster” Gross Anatomy and location From Digital Anatomist “C” shaped structure in medial temporal lobe Morphology Another terminology mess Allocortex/ archicortex 古皮质 Hippocampal formation 海马结构 Dentate gyrus 齿状回 Hippocampus 海马 “Cornu ammonis” 阿蒙氏角 Subicular complex 下托 Entorhinal cortex 内嗅皮质 Hippocampus 1- hippocampal body 2 – head and digitationes hippocampi 3 – hippocampal tail 4 – fimbria (fornix) 海马伞 5 – fornix 穹隆 6 – subiculum 下托 Hippocampus Any sensory stimulus will go to the hippocampus, and from there to the thalamus, hypothalamus and other limbic structures through FORNIX. Stimulation of hippocampus can cause pleasure, rage, sex drive, etc. Important feature of hippocampus is that it creates prolonged response It has only three layered cortex. It has role in learning and memory Neocortex greatest developed in human Hippocampus of Rat Development of Hippocampus From Digital Anatomist From Digital Anatomist Cytoarchitecture Two interlocking cell fields • Dentate gyrus • hippocampus Human Rodent so sp •Stratum oriens 始层 •Stratum pyramidale 锥体层 •Stratum lucidum 透明层 •Stratum radiatum 辐射层 •Stratum lacunosummoleculare 网状分子层 sl sr sl-m ml Hilus CA1-CA3: pyramidal neurons Dentate Gyrus: granule cells Intrinsic connections Cajal, 1901 hippocampal Network: The hippocampus forms a principally uni-directional network, with input from the Entorhinal Cortex (EC) that forms connections with the Dentate Gyrus (DG) and CA3 pyramidal neurons via the Perforant Path (PP). CA3 neurons also receive input from the DG via the Mossy Fibres (MF). They send axons to CA1 pyramidal cells via the Schaffer Collateral Pathway (SC), as well as to CA1 cells in the contralateral hippocampus via the Associational Commisural (AC) Pathway. CA1 neurons also receive inputs direct from the Perforant Path and send axons to the Subiculum (Sb). These neurons in turn send the main hippocampal output back to the EC, forming a loop. Connections Afferents: Much of cortex is reciprocally connected to entorhinal cortex 内嗅皮质 Cholinergic and GABA input via septal nuclei 隔核 Amygdala VTA 中脑腹侧被盖区, LC蓝斑, Raphe n. 中缝核 Efferents Via the fornix 穹隆 Precommissural: septal nuclei Post-commisural: mammillary bodies (to anterior thalamic nucleus via mammillothalamic tract) Two limbic Axis Hippocampal Extroceptive 外感受 Cognitive processeslearning and memory 认知 Receive information from cortical sensory areas Project to ant. Thalamus Ant. Thalamus-cingulate gyrus-hippocampus (Papez circuit) Hippocampus-mammillary body-thalamus Project to basal ganglion Project to mid brain via medial forebrain bundle. Amygdaloid Introceptive内感受 Generation of emotions, motivational states 情感,动机 Cortical sensory areas and internal organs Dorso medial thalamus Dorso medial thalamusprefrontal cortex-amygdala. Amygdala –ventro medial hypothalamus Project to basal ganglion. Project to mid brain via medial forebrain bundle. Part 3. Hypothalamus Limbic system and hypothalamus Hypothalamus 下丘脑 Peptidergic neuroendocrine cells: Magnocellular neurons “Large” neurons Located in paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei Secrete oxytocin and vasopressin into general circulation via posterior pituitary Oxytocin Vasopressin uterine contraction & milk ejection vasoconstriction, water resorption by the kidney Peptidergic neuroendocrine cells: Parvocellular neurons “small” neurons Located in medial basal region, arcuate and tuberal nuclei, periventricular region, preoptic and paraventricular nuclei Secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones into portal vasculature via anterior pituitary Nobel prize awarded to Guillemin (Salk), Schally and Yalow in 1977 for their (independent) work in proving the hypothesis that the hypothalamus releases hormones that regulate the pituitary Portal veins of hypophysis Hypothalamus pathways Afferent Pathway Projecting from Median forebrain bundle Collaterals from other tracts Fornix Hippocampus (to MB) Stria terminalis amygdala Efferent Pathway Projecting to hypothalamicohypophyseal (from supraoptic nuclei) Mammillothalamic tract Neurohypophysis (pituitary) Anterior thalamic nucleus Widespread projections to many brain regions, including the cerebral cortex, via histamine and hypocretin containing neurons in the tuberal region of the hypothalamus Part 4. Cingulate gyus and Parahippocampal gyrus 思考题 简述边缘系统的研究历史 边缘系统包括哪些结构?核心结构是什么? 试述杏仁核的位置、核团分部、纤维联系及功能。 试述海马的位置、分区、细胞构筑、内部通路及 外部纤维联系。 试述下丘脑的位置及其与神经内分泌的关系。 Thanks !