* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Limbic System Limbic `Lobe` Components Limbic System Components
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Adult neurogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Olfactory bulb wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
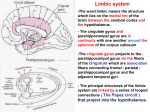
Limbic System Forms a limbus (border) around the brainstem Emotional behavior and memory Limbic ‘Lobe’ Components Limbic System Components Septal Nuclei Amygdala Hypothalamus (mamillary bodies) Thalamus Reticular Formation Epithalamus Frontal cortex Olfactory cortex Ventral striatum Anterior nucleus Medial nucleus 1 Limbic System Functions Emotional behavior Memory Homeostatic responses Survival instinct food Fight or flight Securing Sexual behavior Motivation Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Dentate gyrus Toothed surface Subiculum Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Dentate gyrus Subiculum 2 Hippocampus Archicortex - 3 layers Molecular Pyramidal Compact zone Less compact Superior division Inferior division Multiform Hippocampus - Fields CA1 Superior Sensitive to Temporal lobe epilepsy Anoxia Ischemia Trigger zone CA2 & CA3 CA4 Inferior region Transition between hippocampus and dentate gyrus Hippocampal Neurons Principal neurons Pyramidal Output Apical dendrites Basal dendrites Towards molecular layer Towards ventricular surface Axons Ventricular surface Form Recurrent collaterals Alveus Fornix Molecular layer Multiform layer Excitatory 3 Hippocampal Neurons Intrinsic neurons Polymorphic neurons Irregularity of soma and dendrites Multiform Axons layer to pyramidal cells Arborize around body Aka basket cells Inhibitory Dentate Gyrus 3 layers Molecular Granule Small densely packed granule cells Form mossy fiber system Dentate gyrus to hippocampus Multiform Pyramidal Basket cells Output to hippocampus Subiculum 3 layers Molecular Pyramidal Output through fornix Multiform 4 Hippocampal Formation: Afferents Entorhinal Septal area Contralateral hippocampus Hypothalamus Thalamus Amygdala Locus ceruleus Raphe nucleus Ventral tegmental area Hippocampal Formation: Afferents Entorhinal area Parahippocampal Perforant Perforates subiculum en route to hippocampus & dentate gyrus Alvear gyrus to hippocampal formation Pathway Pathway Smaller Ventricular surface of the hippocampus, near the alveus Most Site heavily damaged in Alzheimer’s of early onset in Alzheimer’s Hippocampal Formation: Efferents 5 Fornix Output of hippocampus Thalamus & hypothalamus Septal region Pyramidal axons Alveus Fimbria Crus of fornix Body of fornix Columns of fornix 75% synapse in mamillary bodies and anterior nucleus of the thalamus 25% synapse in septal nuclei Entorhinal-Hippocampal Circuitry Excitatory synapses Amygdala ‘almond’ shaped nuclei Tip of temporal lobe 6 Amygdala: Afferents Olfactory, somatosensory, auditory, visual Autonomic inputs Integrates Amygdala: Efferents Stria terminalis Main output nuclei Anterior, preoptic, ventromedial nuclei of the hypothalamus Bed nucleus Septal Scattered group of nuclei at the end of the stria terminalis Amygdala: Efferents Ventral amygdalofugal pathway Prefrontal, inferior temporal, insular, cingulate, occipital cortices Ventral striatum Dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus Hypothalamus Septal area Substantia innominata Diffuse cholinergic system Activates cortex in response to significant stimuli Brainstem nuclei involved in visceral functions Dorsol motor nucleus of the vagus, raphe nuclei, locus ceruleus, parabrachial nucleus, etc 7 Amygdala: Functions Autonomic Orienting response Emotional behavior & food intake Happiness, pleasure Hyperphagia lesion: Sluggish, hypoactive Sexual activity High density of sex hormone receptors Bilateral lesions Mostly negative emotions Arousal response Decreased emotional tone, fear sadness aggression Aphagia Basolateral group Emotional & social meaning Corticomedial group of nuclei Facial expression To novel events Heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, gastric motility Hypersexuality Motor activity Related to eating Septal Area 2 divisions Septum pellucidum Glia Separates lateral ventricles Septum verum Septal nuclei Bed nucleus Nucleus accumbens Septal Area: Afferents & Efferents Reciprocal 8 Septal Area: Functions Emotional behavior Stimulation Pleasure Autonomic effects Hyperactivity to novel stimulus, which quickly drops to immobility Learn quickly, perform effectiviely Reward Lesion Over drink Activity Lesion Lesion Learning Rage Water Consumption Lesion Stimulation Inhibit autonomic function Via vagus Limbic Loop: Integrator Takes sensory processing and autonomic/endocrine information Modulates frontal processing Goal: to affect motor behavior Limbic System: Functions Preservation of the individual Flight/fight Eating Drinking Emotional behavior Memory Emotional valence of sensory stimuli Motivation Preservation of the species Sexual Social behavior behavior 9 Memory Explicit/Declarative Episodic (personal experience) – limbic system (knowledge) - neocortex Short-term vs long-term Semantic Implicit Procedural Priming (skill learning) – basal ganglia/cerebellum – sensory association areas Short-lived enhancement following recent exposure to similar material False memories/Deja vu Clinical Correlates Amnesia Retrograde Anterograde Global – acute, transient severe anterograde with varying periods of retrograde Modality-specific – e.g. vision Permanent – e.g. Alzheimer’s Transient – e.g. post-traumatic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Olfactory hallucinations, e.g. smelling burning rubber Gustatory hallucinations, e.g. bad taste Auditory hallucinations Visual hallucinations Rhythmic movements related to feeding Complex motor acts [walking, undressing] Amnesia Aggressive behavior Possibly death due to autonomic [cardiac] control 10 Alzheimer’s Degenerative Severe memory loss Starts as short-term, but accelerates as disease progresses Disorientation to time, place, person Behavioral Depression, paranoia, aggression Alzheimer’s Shrunken gyri in association cortices and limbic system Primary sensory cortices and motor cortex mostly spared Neurofibrillary tangles (tau protein) Senile plaques (betaamyloid) Genetic form Environmental Aluminum? 11