* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
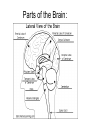
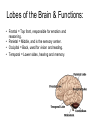
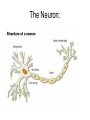
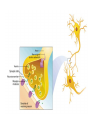
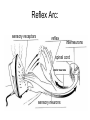
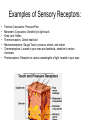
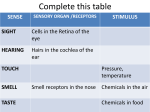
Nervous System In Class Notes By: Mrs. Swineheart's Fifth Hour Function & Divisions: • Functions: o o o sends/recieves information process information sends messages to organs through communication lines called nerves • Divisions (2) o o CNS (central nervous system) bodys main informatoin prcessing center Brain and Spinal Cord PNS (peripheral nervous system) nervous tissue outside of the CNS delivers information to CNS carries messages to organs Brain: Parts & Functions • Brainstem = The lower portion of the brain important for breathing and other vital functions. • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other brain areas. • Cerebellum= Region of the brain that plays an important role in the integration of sensory perception • Hypothalamus = a structure in the brain under the thalamus that monitors activities such as body temperature and food intake. Parts of the Brain: Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. The Neuron: Function of the Neuron: • conducts nerve impulses • transmit signals at a fast rate. • allows signals to transmit at a fast rate through the specific and other locations. From one neuron to the next: Synapse: junction between two neurons or a neuron and another cell or electrical or chemical signals are relayed. Synaptic cleft: tiny space where nerve signal must be transmited. Neurotransmitters: chemical messanger that carries information from one neuron to another or to another cell. • When the action potential reaches the knob, it causes the vestles to release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft.Receptor molecules on the recieving neuron's membrane accept the neurotransmitter. Reflex Arc: • Uses 3 Parts: o o o Sensory Input Integration Motor Output • Examples: o o o Reflex check with doctor and hammer on your knee Touching something hot Feeling pain Reflex Arc: sensory receptors reflex interneurons spinal cord motor neurons sensory neurons Examples of Sensory Receptors: • • • • • • • Pacinian Corpuscles- Pressure/Pain Meissner's Corpuscles- Sensitivity to light touch Knee Jerk- Reflex Thermoreceptors- Detect heat/cold Mechanoreceptors- Gauge Touch, pressure, sketch, and motion Chemoreceptors- Located in your nose and tastebuds, sensitive to certain chemicals Photoreceptors- Receptive to various wavelengths of light, located in your eyes Drugs: • 2 Types: o o Stimulants Usually increase the amount of activity in the CNS increases amount of alertness and heart rate (nicotine) Depressants Slow down CNS activity causes less coordination and impairs judgement (alchohol) Illnesses: • • • • • • • Alzheimers Tourette Syndrome Lou Gehrigs Huntingtons Muscular Dystrophy ADD Etc.