* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous and Endocrine Systems
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
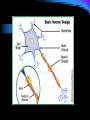
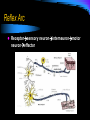
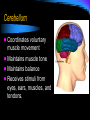
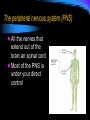
Nervous System Nervous System Responds to stimuli to maintain homeostasis. Stimulus (Stimuli) = a signal to which an organism reacts Response = some action or movement of an organism brought on by a stimulus Nerve cells The cells of the nervous system are called neurons. Neurons carry messages called impulses Nerves = send messages to the spinal cord, muscles, and glands for response The Neuron Cell body (cyton): contains nucleus, cell organelles; site of metabolic activities Nucleus : contains the genetic material Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body The Neuron Axon: carries impulses away from the cell body Schwann cell nucleus Schwann cell: surrounds the axon; produces the myelin sheath The Neuron node of Ranvier: gap between neighboring Schwann cells Myelin sheath: insulation that increases the speed at which the impulse can travel The Neuron Terminal branches the axon terminates (ends) with the terminal branches Synaptic knobs: release neurotransmitters into the synapse The Neuron Synapse: small gap between two successive neurons ***Neurotransmitters are chemicals used to transmit an impulse from the axon of one neuron to the dendrites of the next neuron Types of Neurons Sensory Neurons: transmit impulses from sensory organs (receptors) to the spinal cord and brain Sensory organs: eyes, ears, nose, mouth, skin Types of Neurons Motor Neurons: transmit impulses from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and glands (effectors) Types of Neurons Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons Found ONLY in the Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) Reflex Arc Receptorsensory neuroninterneuronmotor neuroneffector Reflexes Automatic responses to stimuli We do not have to think about the response They are inborn All connections have been formed by the time we are born They are fast They take the shortest path The speed of the response is protective reflex arc animation Central Nervous System Part of the nervous system that contains the brain and spinal cord. The Brain Coordinates all of your body activities The brain is made of 100 billion neurons Interprets stimuli, sends impulses to the body Cerebrum Largest part of the brain Thinking takes place here Controls: Memory Movement Thinking Cerebellum Coordinates voluntary muscle movement Maintains muscle tone Maintains balance Receives stimuli from eyes, ears, muscles, and tendons. Brain Stem Located at the base of the brain Connects the brain to the spinal cord Contains: Midbrain and Pons = pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions Spinal Cord Extension of the brain stem Made of bundles of neurons that carries impulses to all parts of the body The peripheral nervous system (PNS) All the nerves that extend out of the brain an spinal cord Most of the PNS is under your direct control THE PNS Autonomic Nervous System: controls body activities that are involuntary Contractions of heart muscle Movement of smooth muscles Disorders of the Nervous System Alzheimer's Diseases A progressive disease that destroys memory and other important mental functions Brain cell connections and the cells themselves degenerate and die There is no cure Disorders of the Nervous System Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Weakens muscles and impacts physical function Nerve cells break down, which reduces the function of muscles. There is no cure for ALS Disorders of the Nervous System Epilepsy A disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures Can be caused by genetics or a brain injury Treated by medications, surgery, devices, or dietary changes Disorders of the Nervous System Meningitis Infection and inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain or spinal cord Vaccines can prevent some forms of meningitis Depending on the cause, it may get better on its own, or it can be life-threatening Disorders of the Nervous System Multiple Sclerosis Our WBCs attack and destroy Schwann cells This slows down the impulses from neurons