* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Autonomic nervous system
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
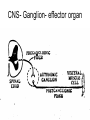
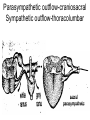
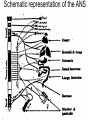
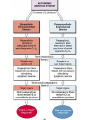
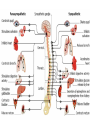
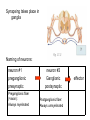
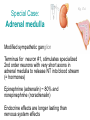
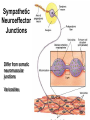
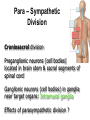
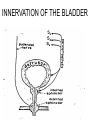
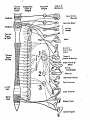
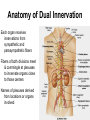
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM BY DR.A.A.OREMOSU DEARTMENT OF ANATOMY CMUL Overview of ANS Pathway for Visceral Motor Output ANS has two antagonistic divisions: 1. Sympathetic 2. Parasympathetic ANS output always involves two neurons between spinal cord (CNS) and effector. • Nerve supply of visceral structures • Sympathetic- fright or flight response • Parasympathetic- recovery from flight/fright response • CNS-gnaglion- effector organ • Sympathetic also supplies blood vessels of skin, arector pili muscles, arterioles & sweat glands CNS- Ganglion- effector organ Ganglia • Lie outside CNS • Sympathetic-ganglia are in (a) sympathetic chain & (b) ganglia around large arteries • Parasympathetic- ganglia present ON or IN organ which they supply • Preganlionic fibres- white rami • Postganglionic fibres- gray rami Parasympathetic outflow-craniosacral Sympathetic outflow-thoracolumbar Thoraco lumbar out flow • T1- L2(3) • Supplies almost all viscera • Sympathetic chain 3 cervical, 10-12 thoracic, 4 lummbar, 4-5 sacral, I coccygeal ganglia • The 2 chain unite @ ganglion impar in front of coccyx Schematic representation of the ANS Synapsing takes place in ganglia ? Fig 17.3 Naming of neurons: neuron #1 preganglionic presynaptic Preganglionic fiber (=axon): Always myelinated neuron #2 Ganglionic postsynaptic Postganglionic fiber: Always unmyelinated effector Sympathetic Division Thoracolumbar division Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located between T1 & L2 of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near vertebral column Paravertebral ganglia = sympathetic chain ganglia Prevertebral ganglia = collateral ganglia Special case: adrenal medulla Effects of Sympathetic Division? The splanchnic nerves • Greater splanchnic(GS) T5-9 • Lesser splanchnic (LS) T10-11 • Least splanchnic (LeS) T12 Fibres pass through sympathetic chain without relaying End in ganglia GS-coeliac LS-superior mesenteric LeS-may be absent-superior mesenteric Special Case: Fig. 17-6 Adrenal medulla Modified sympathetic ganglion Terminus for neuron #1, stimulates specialized 2nd order neurons with very short axons in adrenal medulla to release NT into blood stream (= hormones) Epinephrine (adrenalin) ~ 80% and norepinephrine (noradrenalin) Endocrine effects are longer lasting than nervous system effects Sympathetic Neuroeffector Junctions Differ from somatic neuromuscular junctions Varicosities Summary of Sympathetic Division A. Neuron #1 is short, neuron #2 is long B. Synapsing occurs in prevertebral chain ganglia or paravertebral collateral ganglia C. Neuron #1 releases Ach, usually neuron #2 releases NE D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent Para – Sympathetic Division Craniosacral division Preganglionic neurons (cell bodies) located in brain stem & sacral segments of spinal cord Ganglionic neurons (cell bodies) in ganglia near target organs: Intramural ganglia Effects of parasympathetic division ? Craniosacral outflow • Cranial nerves 3,7,9,10 • Nucleus, nerve, ganglion & organ supplied • Nuclei are Edinger westphal, superior salivatory, inferior salivatory, dorsal motor nucleus of vagus respectively • Ganglia ciliary-CN-III • Sphenopalatine-CN VII • Submandibular- CN VII • Otic -CN IX • Numerous(thorax,abd.)- CN X PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION • III-Supply intrinsic eye muscles • VII-Glands of nose, mouth & pharynx • VII & IX-Salivary glands • V-Organ- heart, respiratory system, abdominal viscera Sacral part • Nervi eregentes- wandering nerves • Supplies pelvic viscera • Produces erection in males • Relaxes internal urethral sphincter • Root value S2,3,4 • Stimulation empties bladder INNERVATION OF THE BLADDER Summary of Parasympathetic Division A. Neurons #1 are long, come from the brain stem or sacral spinal cord, run with the spinal or pelvic nerves and produce ACh. B. Neurons #2 are short, produce ACh, and may be either excitory or inhibitory. Anatomy of Dual Innervation Each organ receives innervations from sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers Fibers of both divisions meet & commingle at plexuses to innervate organs close to those centers Names of plexuses derived from locations or organs involved Thank you, but don’t forget that networking will be for your corporate good!