* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Anatomy & Physiology I
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
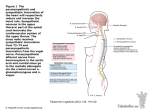
Autonomic Nervous System 11 Unit 1 Chapter 11 Comparison 11 • Somatic systems- conscious awareness • Autonomic sensory - not consciously perceived • Autonomic motor- cardiac muscle, smooth muscle & glands Unit 1 Monitors internal conditions- blood gasses, viscera operation, etc Often adjustment of internal controls in relation to whole body needs • Somatic motor neurons go directly from spinal cord to skeletal muscle • Autonomic motor systems includes two motor neurons: • Preganglionic neuron from CNS to autonomic neuron from cell body in ganglion to effector 11 Unit 1 Motor pathways • Sympathetic division • Parasympathetic division • both divisions often innervate the same effector • They have opposite effects • E.g. sympathetic stimulates heart rate and parasympathetic slows it 11 Unit 1 Divisions Figure 11.1a Figure 11.1b Sympathetic division 11 • Thoracolumbar division• Preganglionic fibers – • From lateral horns via ventral roots • to sympathetic ganglia • synapse with postganglionic cells in ganglia Unit 1 outflow from thoracic & lumbar segments of spinal cord Sympathetic Ganglia 11 • Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia Vertical rows on either side of vertebral column Post synaptic fibers mostly got to organs above diaphragm Anterior to vertebral columnceliac, superior mesenteric & inferior mesenteric Innervate organs below diaphragm Unit 1 • Prevertebral ganglia • • • • • To postganglionic neuron 1. in trunk ganglion at level of root 2. In ganglion higher or lower in chain 3. in prevertebral ganglion 4.Directly to target organ-adrenal medulla average preganglionic neuron synapses with 17 postganglionic neurons 11 Unit 1 Preganglionic Routing Figure 11.2 Parasympathetic Neurons 11 • Output at top-medulla nuclei Cranial nerves II, VII,IX, X Near or in the innervated organ • localized to single effector organ Unit 1 • Bottom of spinal cord- sacral nerves • Synapse in terminal ganglia Figure 11.3 Neurotransmitters 11 • Acetylcholine- • NorepinephrineMost postganglioic sympathetic terminals Longer effects Amplified by adrenal release with epinephrine Unit 1 All preganglionic fibers terminals parasympathetic postganglionic terminals A few postganglionic sympathetic terminals Short-lived effects ANS Activity 11 Sweat glands, arrrector pili muscles, kidneys, spleen, blood vessels & adrenal medulla Unit 1 • Balance between sympathetic & parasympathetic “tone” regulated through hypothalamus • Only sympathetic to: Sympathetic Effects 11 Dilate pupils Increase HR, heart contraction & BP Dilate airways Constrict blood vessels to non essential organs: kidneys, GI tract Dilate vessels to muscles, cardiac muscle, liver & adipose Mobilize nutrients: glucose & fats Unit 1 • fight-or-flight activities Parasympathetic Effects 11 Salvation Lacrimation Urination Digestion Defecation Decrease- HR, airway diameter, pupil diameter Unit 1 • Rest-and–digest act ivies • SLUDD