* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro-biological
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
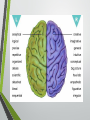
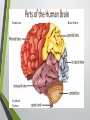
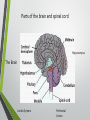
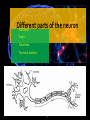
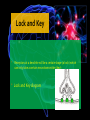
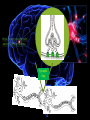
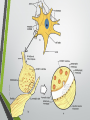
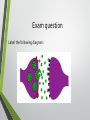
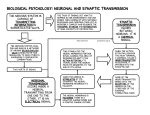
Biological Psychology Introduction to Biological Psychology CSN Structure of the Brain Role of the Neuron The Function of Neurotransmitters Synaptic Transmission Biological psychology • What is Biological psychology? • What are the main assumptions of Biological psychology? • What do we need to know? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hy1H5uFzZJs What is Biological psychology? • It looks at chemical activity in the brain (neurotransmitters) . • It looks at how messages are transmitted through hormones. • It looks at how characteristics are inherited via genes (evolutionary perspective). Key Assumptions • Behaviour can be explained with reference to specific structures in the brain. • Aspects of behaviour can be explained by the action of neurotransmitters. • Behaviour can be explained with reference to human evolutionary history. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • The Nervous System has 2 main parts – the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System. • The CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord. • The brain is within the skull and the spinal cord is within the vertebrae. CNS • The CNS is the main control centre of the body—it takes • • • • in sensory information, organizes and synthesizes data, then provides direction for motor output to the rest of the body. The CNS is made up of the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord. The brain is the main data centre of the body and consists of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning such as thought, and the cerebellum which maintains coordination. The brain stem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body's main receptors, and serves as a conduit for sensory input and motor output. What happens when brains get ‘broken’? • Read the two articles ‘Phineas Gage and the effect of an iron bar through the head on personality’ • and ‘'There was a lot more to fix than I thought‘. • What do these articles tell us about the structures and functions of the brain? • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8NtmDrb_qo Cerebrum Cerebral Cortex Brain Stem • Find out the location and function of the following brain parts: • • • • • • • • • Pre-frontal cortex Corpus callosum Limbic System Ventricles Thalamus Amygdala Hippocampus Hypothalamus Midbrain • If you cannot find the location just define. Stretch and challenge: Find out about 5 other brain structures and their functions. Stretch and challenge: Research 1 example of brain injury and how this has affected the individual’s functionality. Parts of the brain and spinal cord Hippocampus The Brain Limbic System Prefrontal Cortex Describe the structure and role of a Nueron What is a neuron? • Cell in nervous system which sends processes and sends information within the body. • Sensory neurons • Receive messages from senses • • • Touch Light Sound • Motor neurons • Muscle movement Different parts of the neuron • Cell body • • • Axon Dendrites Terminal buttons How brain messages are sent using neurons Messages in the brain are sent by using electrical impulses and chemicals called neurotransmitters How brain messages are sent using neurons • Step one: • In one neuron, in the cell body, an electrical impulse (can also be called an action impulse) is triggered. This travels down the axon to the end. How brain messages are sent using neurons • Step two: • At the end of the axon and the terminal branches are the terminal buttons here the electrical impulse releases a chemical called a neurotransmitter How brain messages are sent using neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that act between the neurones in the brain. This allows the brain to process thoughts and memories. Dopamine Serotonin Noradrenaline Acetylcholine How brain messages are sent using neurons • Step three: • This neurotransmitter now has to cross a gap called a synapse or a synaptic gap to get to the dendrites on the next neuron to continue the message. The neurotransmitter can get lost in the gap. How brain messages are sent using neurons • Step four: • If the receptors at the dendrites of the next neuron are suitable to receive the neurotransmitter in the gap it will get picked up by them. LOCK AND KEY Lock and Key • Receptors at a dendrite will be a certain shape (a lock) which can only take a certain neurotransmitter (key) • Lock and Key diagram How brain messages are sent using neurons • Step five: • The neurotransmitter changes the chemical balance (this is called the synaptic transmission) at the receptor which sets off an electrical impulse whilst the neurotransmitter drops back into the synaptic gap. And the process starts all over again! WHEW! Stop and make sure we understand Label the structure of a neuron. Exam Prep Describe the role of a neuron. Describe the process of synaptic transmission. First a quick recap! https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=WhowH0kb7n0 Synaptic Gap Exam question Label the following diagram: • • • • • • • Place the following in the correct order The axon terminal of one neuron reaches the dendrites of another. Dendrites surround the nucleus which is connected to a long extension called an axon, which reaches the axon terminal. On one side, at the dendrites, there are receptors of a certain shape, prepared to receive the neurotransmitter from another neuron. If the neurotransmitter fits the receptor the message is passed on; if it does not, the message is blocked. Between the terminal and the dendrites, there is a gap called a synapse. A neurotransmitter travels down the pre synaptic neuron, across the synapse and binds in a lock and key effect to a receptor on the post synaptic neuron. A neuron is made up of dendrites, a nucleus, an axon and an axon terminal. Describe the process of synaptic transmission.