* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 PowerPoint Outline
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
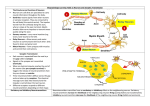
General Psychology Chapter 3 / PowerPoint Outline Biological Foundations of Behavior Neurons: Workhorses / Building Blocks of the NS Neurons: individual cells in the NS that receive, integrate and transmit information o Soma or Cell body: processing center o Dendrites: receive messages [‘tree’] o Axon: sends messages o Myelin sheath: insulates axon o Nodes of Ranvier: speed up signal Glial Cells: The ‘Other Stuff’ in the NS Provide structure for the NS [Glial = ‘glue’] Ratio of glial cells to neurons = 10:1 Approximately 50% of brain volume Nourish neurons, remove waste, insulate, help brain develop prenatally Action Potential of a Neuron Neuron at resting state: slight negative charge (-70 mV) inside of cell o More negatively charged chloride ions inside cell o More positively charged sodium and potassium ions outside of cell Excitatory neurotransmitters received at dendrite receptor sites Causes change in permeability of cell membrane allowing positively charged ions to enter cell Voltage in cell goes from negative (-70 mV) to slightly positive (+30 – 40 mV) when neuron fires (1 – 2 milliseconds) Cell firing followed by refractory (‘recovery’) period (1 – 2 milliseconds) before returning to resting potential Entire action potential process takes an approximate average of 6 – 7 milliseconds The All-or-None Law Neurons either fire at 100% strength or not at all Neurons convey differing signal strengths by firing at different rates Example: o Dim lights trigger 5 APs per second o Bright lights =100 – 200 APs / second Synaptic Transmission Action potential charge reaches axon terminal (tip) Synaptic vesicles generate and store neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) Vesicles in axon terminal fuse with membrane, burst open releasing neurotransmitters into synapse Neurotransmitters cross synapse and potentially bind in matching receptor site on dendrite of neighboring neuron Following transmission of message, the synapse may be ‘cleaned up’ by o Destructive enzymes (MAOs) that clear away excess neurotransmitters o Taken back into axon terminal through amine pumps in the process of ‘reuptake’ Drug Effects Agonist drugs: make transmission easier by mimicking a neurotransmitter, speeding up release, blocking reuptake, or possibly by sensitizing the receptor site Antagonist drugs: make transmission more difficult by slowing transmission, or possibly by desensitizing receptor site by making the receptor site chemically less sensitive to an incoming neurotransmitter Neurotransmitters Norepinephrine In the brain causes excitation In the body, either excitation or inhibition Linked to / created out of dopamine Associated with heightened arousal, consciousness and the experience of pleasure Low levels associated with depression o Symptoms of Depression [will not be tested over these symptoms until Test 4 over Chapter 15] Sad, depressed mood Sleep disturbance Appetite disturbance Fatigue, loss of energy Psychomotor retardation or agitation Inability to focus or concentrate Excessive guilt or hopelessness Thoughts of suicide, suicide plan or attempt Loss of interest and pleasure in life Dopamine Found in the brain, inhibitory in nature Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with schizophrenia o Schizophrenia Symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought processes, break from reality Causes: complete cause is unknown Genetics play a notable role (twin studies) High levels of dopamine transmission at synapse Treatment: anti-psychotic medication Anti-psychotic drugs act as a dopamine antagonist by inhibiting receptor sites Serotonin Found in brain & spinal cord, inhibition Linked with arousal & consciousness, sleep cycle, appetite, regulation of mood, moderation of aggression Unregulated levels associated with mood, eating and anxiety disorders (OCD) Low levels associated with depression o Also eating disorders and OCD SSRI drugs used to treat depression block serotonin reuptake [agonist] Acetylcholine In the brain, excitation In the body, excitation or inhibition Linked with stimulation of muscle movement o Curare blocks ACh receptors / causes paralysis [ACh antagonist] o Botox blocks ACh receptors temporarily paralyzing facial muscles to reduce wrinkling In the brain, associated with thinking and memory function o Nicotine mimics ACh at receptors sites [ACh agonist] Abnormally low levels associated with Alzheimer’s disease o Alzheimer’s Disease Most common form of dementia Dementia: memory impairment and other problems of language, thinking & movement Cause: fairly genetic in origin Healthy brain cells degenerate to cellular plaques Treatment: Aricept & Cognex act as an agonist for acetylcholine GABA: Gamma Amino Butyric Acid Found widely through brain / NS [40%] Found in brain, spinal cord, inhibition Serves to help control uncontrolled muscle movement Abnormally low levels associated with Huntington’s Disease Anti-anxiety drugs like Valium work as an agonist for GABA causing a slowing of neural function Divisions of the Nervous System The Brain Methods of Brain Study EEG Lesioning Electrical Stimulation Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Imaging o CT, PET, MRI, fMRI Brain Overview [1] Medulla: -Blood circulation -Breathing -Muscle tone -Reflexes Cerebellum: -Coordinates movement -Balance -Posture -Thought organization -Damage = fine motor -1st part depressed by ETOH Pons: -L/R coordination -Sleep -Bladder Brain Overview [2] Amygdala / Hippocampus / Hypothalamus Amygdala: • Major emotion center, especially fear from threat • Plays a role in memory, decision making Hippocampus: • Primary memory processing center Hypothalamus: Motivation [food, water, sex] Emotion [pleasure, anger/rage] Sleep cycle, blood pressure Pleasure Center Self-Stimulation of a Rat Video: https://youtu.be/aNXhyPj-RsM Comparing Animal and Human Brains Lobes of the Cerebrum Mirror Neurons [Giacomo Rizzolatti]: • Neurons activated by performing an action or by observing someone perform an action • Thought to play a role in mimicry and empathy • Mirror neuron deficits are implicated in autism Left Brain – Right Brain Functions Left-Right Hemispheric Variation Functions generally based in left / right brain anatomy: Left: Analytical functions Math Language / Grammar Time Right: Artistic Visual Spatial Creative Split Brain Research [Roger Sperry / Michael Gazzaniga] Rarely performed treatment for severe, uncontrolled epilepsy Corpus callosum is severed separating left / right hemispheres L-R hemispheres no longer communicate directly Yet, sensory-motor functions are still linked to L-R sides of body Left-Right Brain Conclusions Measured L-R brain difference do exist For most, the two sides are well integrated Many researchers contend L-R brain differences are overblown No evidence to support claim that some are ‘left’ or ‘right-brained’ fMRI studies show no distinct L-R differences in brain activity between L-R brain styles Yet, L-R cognitive styles do exist