* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the brain and behaviour
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
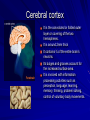
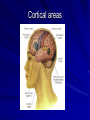
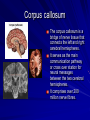
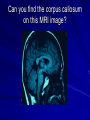
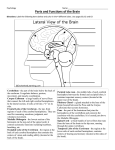
Introduction to the brain and behaviour Amazing brain facts Cerebral cortex Cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum Amazing brain facts Your skin weighs twice as much as your brain. Your brain uses 20% of total oxygen pumping around your body. 750ml of blood pumps through your brain every minute It consists of 100 billion neurons. Time until unconsciousness after loss of blood supply to brain is 8 – 10 secs. Approximately 75% of it is water. If you could harness the power used by your brain you could power as a 10 watt light bulb! Male brain Female brain Cerebral cortex It is the convoluted or folded outer layer or covering of the two hemispheres. It is around 2mm thick It contains ¾ of the entire brain’s neurons. Its bulges and grooves account for the increased surface area. It is involved with information processing activities such as perception, language, learning, memory, thinking, problem solving, control of voluntary body movements. The cerebral cortex It is believed that the size of a species’ cerebral cortex is linked to intellectual ability. The bigger the cerebral cortex, the more capable the organism is of intelligent behaviour such as thinking, problem solving and decision making. Homer Simpson’s Brain Four cortical lobes Cortical areas Cortical areas 1. Sensory cortex areas – receive and process information from the senses. 2. Motor cortex area – receives, processes and sends information about voluntary bodily movements. 3. Association cortex areas – integrate sensory, motor and other information and are involved in complex mental abilities. Cerebral hemispheres These are the two almost symmetrical brain structures that appear to be separated by a deep groove (longitudinal fissure) running from the front to back of the brain. They are connected at several points by strands of nerve tissue. They are referred to respectively as the left and right hemispheres. While they share some common functions, they also have specialised functions. Eg. the left hemisphere receives sensory information from the right side of the body and controls movements on the right side. Left hemisphere is primarily involved with language, right hemisphere is primarily involved with spatial tasks and recognition of faces. Corpus callosum The corpus callosum is a bridge of nerve tissue that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres. It serves as the main communication pathway or cross over station for neural messages between the two cerebral hemispheres. It comprises over 200 million nerve fibres. Can you find the corpus callosum on this MRI image? Sample exam questions Question 1 (VCAA 2005) The major function of the corpus callosum is to A. coordinate autonomic functions such as breathing and heart rate. B. connect the somatosensory cortex to the motor cortex. C. transfer information between the right and left hemispheres. D. connect Wernicke’s area to Broca’s area. Sample exam questions Question 1 (VCAA 2005) a. The deeply furrowed or grooved layer of tissue that covers the cerebral hemispheres is known as the __________________. (1 mark) b. List two main functions of this grooved layer of tissue. 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ (2 marks) Sample exam questions Question 1 (Checkpoints 2006) What purpose is served by the convolutions in the cerebral cortex of the brain? A. They allow more blood to flow to the neurons as the brain requires more oxygen and nutrients than other organs of the body. B. They provide some protection against injury by acting as a shock absorber if the brain is jolted. C. They allow the brain more room to grow because they progressively unfold as the person ages. D. They give the brain a larger surface area which means more neurons can be packed into a smaller area. Sample exam questions Question 1 What is the ‘corpus callosum’? __________________________________ (1 mark) What is its main function? __________________________________ (1 mark) Sample exam question from VCAA 2006 Question 1 The cerebral cortex A. acts as a protective layer covering the brain. B. connects the right hemisphere with the left hemisphere. C. is responsible for voluntary muscle movements. D. increases the strength of the immune system. Question 2 The cerebral cortex is approximately ____________ thick. A. 2 to 5 millimetres B. 6 to 10 millimetres C. 2 to 5 centimetres D. 6 to 10 centimetres Question 3 The ________________ is a band of nerve fibres connecting the left and right hemispheres. A. cerebral cortex B. cerebral hemisphere C. corpus callosum D. cerebellum