* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
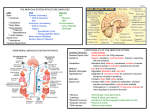
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this document to write a description for the terms you used in the activity. As you conduct the Structures of the Nervous System activity, follow along with this Word document and fill in the descriptions of those terms you used to label the structures. All of the terms in the activity are listed here, but you only need to provide descriptions for those you used. Term Central nervous system Cell body Peripheral nervous system Description CNS is a part of the nervous system of all vertebrates. It is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and skull). PSY 240 Dendrites Dendrites receive information from other neurons through their short processes. Somatic nervous system Axon The axon is the nerve fiber long process structure that carries information from the cell body. Buttons The buttons are located at the ends of axon branches. The buttons release chemicals into the nerve synapse. Autonomic nervous system Synapses This is the space between two neurons. Chemicals are transmitted across the synaptic gap. Dura mater meninx A protective membrane. It is the outermost layer of the brain and one of three such protective membranes. The part of the midbrain that is made up of the tectum and the tegmentum. Mesencephalon Arachnoid meninx The middle one of the protective membranes of the brain. It lies just above the subarachnoid space. Cerebrospinal fluid This fluid serves as a protective cushion and support for the CNS. Diencephalon Located in the forebrain. It is made up of the thalamus and hypothalamus. Pia mater meninx The innermost of the three protective membranes of the brain. It lies between the subarachnoid space and the brain’s cortex. Cerebral ventricles Telencephalon Located in the forebrain. It is the largest single part of the brain. It controls most of our complex functions, including sensory information processing and cognitive processes, as well as involuntary movement. Metencephalon Located in the hindbrain. It is made up of a number of tracts and is responsible in part for reticular formation. Brain stem Basal ganglia Myelencephalon The other part of the hindbrain. It is made up of large tracks that serve to carry signals between the brain and the body. PSY 240