* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous system slides
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
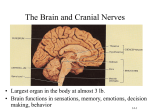
Nervous System • Central Nervous System – Brain – Spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System – Sensory – Motor ¾ The starts off with three simple parts and develops into five complex regions with their own functions. http://www.msu.edu/course/asc/333/casby/NeuroPrimer.html Human Brain • • • • Largest Brain to body ratio (w/w) Average weight 1.4 kg Over 1 billion neurons Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) with a half life of about 3.5 hours ¾ Functions: data conduction & : automatic activities essential for survival ¾ Made up of: the medulla oblongata, pons, & midbrain ¾Medulla & pons: conduct sensory & motor signals between the spinal cord & upper brain : control involuntary actions ¾Midbrain: receives, integrates, & projects sensory information upper brain ¾ Functions: controls coordination of movement & balance : helps vertebrate learn and memorize motor responses ¾Function: site of prominent neural processing & integrating centers ¾Made up of: the epithalamus, hypothalamus, & thalamus ¾ Thalamus: directs neural input from the body to specific areas of the cerebral cortex (the outer, gray area) ¾Hypothalamus: produces hormones : regulates - survival mechanisms - circadian rhythms - sexual & fight-or-flight responses ¾ Function: has the most complex integrating centers ¾ Divided into the left & right cerebral hemispheres, which consist of : the cerebral cortex (right & left sides held together by corpus callosum) : white matter : basal nuclei (motor coordination centers) ¾ The right & left sides of the cerebral cortex each have four lobes. ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ¾ Some aspects of brain research that are interesting include: arousal & sleep; lateralization, language, & speech; emotions; memory & learning; and consciousness. ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytical ability, while spatial perception and artistic ability predominate the right. ¾ Parts of the diencephalon and inner portions of the cerebral cortex (amygdala & hippocampus) form the center where human emotions arise and memory is retrieved and processed. ¾ There is long-term & short-term memory. ¾Consciousness is when you can be aware of your surroundings and make conscious judgments about it.