* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14-1
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
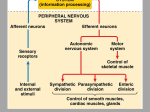
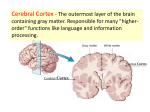
The Brain and Cranial Nerves • Largest organ in the body at almost 3 lb. • Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 14-1 Principal Parts of the Brain • Cerebrum • Diencephalon – thalamus & hypothalamus • Cerebellum • Brainstem – medulla, pons & midbrain 14-2 Protective Coverings of the Brain • Bone, meninges & fluid • Meninges same as around the spinal cord – dura mater – arachnoid mater – pia mater 14-3 Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes • Blood-brain barrier (BBB) – protects cells from some toxins and pathogens • proteins & antibiotics can not pass but alcohol & anesthetics do – tight junctions seal together epithelial cells, continuous basement membrane, astrocyte processes covering capillaries 14-4 Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • 80-150 ml (3-5oz) • Clear liquid containing glucose, proteins, & ions • Functions – mechanical protection • floats brain & softens impact with bony walls – chemical protection • optimal ionic concentrations for action potentials – circulation • nutrients and waste products to and from bloodstream 14-5 Origin of CSF • Choroid plexus = capillaries covered by ependymal cells – 2 lateral ventricles, one within each cerebral hemisphere – 3rd ventricle – 4th ventricle 14-6 Brain Stem Medulla Oblongata Pons Midbrain 14-7 Ventral Surface of Medulla Oblongata • Ventral surface bulge – pyramids – large motor tract – decussation of most fibers • left cortex controls right muscles 14-8 Reticular Formation • Scattered nuclei in medulla, pons & midbrain • Reticular activating system – alerts cerebral cortex to sensory signals (sound of alarm, flash light, or intruder) to awaken from sleep – maintains consciousness & helps keep you awake with stimuli from ears, eyes, skin and muscles • Motor function is involvement with maintaining muscle tone 14-9 Cerebellum • 2 cerebellar hemispheres • Function – correct voluntary muscle contraction and posture based on sensory data from body about actual movements – sense of equilibrium 14-10 Diencephalon Surrounds 3rd Ventricle • Surrounds 3rd ventricle • Superior part of walls is thalamus • Inferior part of walls & floor is hypothalamus 14-11 Thalamus • 1 inch long mass of gray mater in each half of brain • Relay station for sensory information on way to cortex • Crude perception of some sensations 14-12 Hypothalamus • Mammillary bodies are relay station for olfactory reflexes; infundibulum suspends the pituitary gland • Major regulator of homeostasis – receives somatic and visceral input, taste, smell & hearing information; monitors osmotic pressure, temperature of blood 14-13 Functions of Hypothalamus • Controls and integrates activities of the ANS which regulates smooth, cardiac muscle and glands • Synthesizes regulatory hormones that control the anterior pituitary • Contains cell bodies of axons that end in posterior pituitary where they secrete hormones • Regulates rage, aggression, pain, pleasure & arousal • Feeding, thirst & satiety centers • Controls body temperature • Regulates daily patterns of sleep 14-14 Epithalamus • Pineal gland – endocrine gland the size of small pea – secretes melatonin during darkness – promotes sleepiness & sets biological clock • Habenular nuclei – emotional responses to odors 14-15 Cerebrum (Cerebral Hemispheres) • Cerebral cortex is gray matter overlying white matter – 2-4 mm thick containing billions of cells – grew so quickly formed folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci or fissures) • Longitudinal fissure separates left & right cerebral hemispheres • Each hemisphere is subdivided into 4 lobes 14-16 Limbic System • Emotional brain--intense pleasure & intense pain • Strong emotions increase efficiency of memory 14-17