* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14_brain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
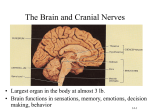
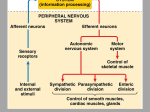
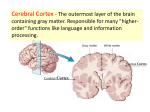
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain – Introduction – Development of brain Embryology – Anatomy of brain Parts and functions The Brain Introduction to the Brain – Weighs about 3 lbs. in adults – Structures Divided into 3 general areas – Functions Controls the bare necessities of life Location for primal drives and emotions Intellectual thought, imagination, perception, interpretation, etc. Human Development – First two weeks – neural tube forms – 4th week - anterior end of the neural tube forms the forebrain midbrain hindbrain Embryology – 3-4 Weeks Embryology – 4 Weeks Embryology – 5 Weeks Embryology – 11 Weeks A Child’s Brain Adult Brain – Forebrain Cerebrum Thalamus & hypothalamus – Midbrain – Hindbrain Cerebellum & pons Medulla oblongata Adult Brain Protections and Coverings – Cranial bones – strong support – Cranial meninges – shock absorbers Dura mater Arachnoid Pia mater The Cranial Meninges The Ventricles of the Brain – Hollow areas within the brain Connect to spinal canal and space around the brain – Cerebrospinal fluid circulates around the brain, down through the ventricles, and into the spinal cord. Ventricles of the Brain Ventricles of the Brain Cerebrospinal Fluid – Composition Clear, colorless, watery Contains proteins, glucose, urea, salts Contains white blood cells – Functions “Floats” the brain Medium of transport Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Problems Associated with CSF – Hydrocephalus – Meningitis – Headaches Hydrocephalus Blood-Brain Barrier – A function of glial cells Secrete chemicals that maintain the BBB Absorb materials from blood Extract materials from brain – Cells of capillaries form tight junctions – Differential rates of passage of certain materials Blood-Brain Barrier The Parts of the Brain Forebrain Cerebrum, Hypothalamus, Thalamus Cerebrum – Gray & White Matter – Outer layer – cerebral cortex Gray matter – Inner portion White matter Masses of gray matter – cerebral nuclei Cerebrum – Gray & White Matter Cerebral Cortex – Gyri are separated by grooves (sulci) Fissures – deeper grooves – Divided into cerebral hemispheres Gyri & Sulci Cerebral Cortex – Divided into lobes – Well mapped Decision-making, planning, personality Primary motor cortex Primary sensory cortex Cerebral Lobes Homunculus Primary Motor Cortex Primary Sensory Cortex Cerebral Nuclei – Collections of cell bodies (gray matter) – Mostly control the movement of skeletal muscles Cerebral Nuclei Limbic System – Functional unit (not anatomical) – Emotional part of the brain Feelings of fear, loss, love, rage, etc. – Includes parts of several anatomical structures Cerebrum Hypothalamus Thalamus Limbic System Hypothalamus – Initiates primal drives Hunger, thirst, sex, rage, etc. Controls autonomic nervous system – “fight or flight” sympathetic response. – Controls pituitary gland (“master gland” of endocrine system) Infundibulum (“funnel”) funnels secretions to the pituitary gland Hypothalamus – Location – under thalamus – Structure Clusters of nerve cell bodies – Autonomic centers Infundibulum Hypothalamus Thalamus – Functions as a relay station between the body and the cerebral cortex Inform us of our emotional state Relay information concerned with motor requirements & actions Integrate visual and auditory reflexes The Thalamus Thalamus Epithalamus – Location Above thalamus – Contains the pineal body Secretes melatonin Midbrain Midbrain – Relay station – Tracts of motor and sensory neurons – Contains nuclei Substantia nigra secretes dopamine – Modifies muscle tone & motor activity – Parkinson’s disease Midbrain Hindbrain Cerebellum, Pons, & Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum – 2nd largest structure of the brain – Divided into 2 lateral hemispheres – Cortex – gyri & sulci Gray matter – Interior White matter – Cerebellar nuclei – deep within white matter Gray matter Cerebellum – Functions – controls subconscious movements in skeletal muscle Coordination Posture Balance Cerebellum, Pons, Medulla Oblongata Pons – Pons = “bridge” Connects the spinal cord with the brain and parts of the brain with each other Consists mostly of white fibers – Functions Controls respiration rate (with medulla) Medulla Oblongata – Continuation of spinal cord – Functions Maintains wakefulness and alertness Contains reflex centers – Cardiac center, vasomotor center, respiratory rythmicity center – Other nonvital centers Medulla Oblongata Cranial Nerves Introduction to Cranial Nerves – 12 pairs – Leave the skull through foramina – Types Mixed Sensory Motor – Part of the somatic nervous system – Innervate organs in head, neck and upper thorax The Cranial Nerves