* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 2 neurotrans and nervous sys
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
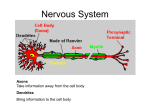
TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS Acetylcholine (ACH) • Deals with motor movement and memory. • Too much and you will…. • Too little and you will… • Lack of ACH has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Serotonin • Involved in mood control. • Lack of serotonin has been linked to clinical depression. Dopamine • Deals with motor movement and alertness. • Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson’s disease. • Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins • Involved in pain control. • Many of our most addictive drugs deal with endorphins. Select Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine (Ach) – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizures, tremors, insomnia) Norepinephrine – Involved in arousal, mood, and sympathetic nervous system activation (Bipolar) Endorphins – elevate pleasure/mood and reduce pain, act by either increasing or decreasing specific NT activity, mimic effects of opium based drugs like morphine Neural Communication Serotonin Pathways Dopamine Pathways Drugs can be….. • Agonists- make neuron fire • Antagonists- stop neural firing • Reuptake Inhibitors- block reuptake Some Drugs work on receptors • Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters • Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT – e.g. beta blockers (Beta blockers block the action of epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) part of the sympathetic nervous system which mediates the "fight or flight" response.) • Agonists : fit receptor well and act like the NT – e.g. nicotine Neural Communication Neurotransmitter molecule Receptor site on receiving neuron Receiving cell membrane Agonist mimics neurotransmitter Antagonist blocks neurotransmitter Neural Communication: The Neural Chain Neurons and Synapses Types of Neurons Sensory Motor Interneurons Motor Neurons • Nerves that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system • Carries messages from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of your body Sensory Neuron Brain Spinal Cord Motor Neuron Sensory Neurons • Nerves that carry incoming information to the central nervous system Sensory • Connect the Neuron sense organs to the brain and spinal cord Brain Spinal Cord Interneurons • Connect the other 2 neurons. Only found in the brain and spinal cord. Sensory Neuron Brain Spinal Cord Motor Neuron A Neural Chain The Structure of the Nervous System A Simplified Neural Network Neurons that learn to work together as a team. The Nervous System Nervous System the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system consists of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems Nerves neural “cables” containing many axons part of the peripheral nervous system connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) All nerves that are not encased in bone Everything but the brain and spinal cord the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to muscles and organs (Peripheral = outer region) Divided into two parts Somatic Autonomic The Nervous System Subparts of the nervous system Somatic Nervous System • Controls voluntary muscle movement • Uses motor neurons Autonomic Nervous System • Controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs • Monitors the autonomic functions • Controls breathing, blood pressure, and digestive processes • Divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Sympathetic Nervous System • The part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats – Automatically accelerates heart rate, breathing, dilates pupils, slows down digestion • Fight or flight response Parasympathetic Nervous System • Automatically slows the body down after a stressful event – Calms the body – Heart rate and breathing slow down, pupils constrict and digestion speeds up Reflexes • Normally, sensory (afferent) neurons take info up through spine to the brain. • Some reactions occur when sensory neurons reach just the spinal cord. • Survival adaptation. The Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System The Endocrine System Endocrine System A second type of communication system in the body made up of a network of glands that produce hormones-- chemical messengers that circulate in the blood • Examples of hormones: – – – – Estrogen/testosterone Thyroid growth hormone follicle-stimulating hormone Hormone • Chemical messengers produced by the endocrine glands and circulated in the blood • Similar to neurotransmitters in that they are also messengers • Slower communication system, but with longer lasting effects Hormones Neurotransmitters Endocrine System/ Endocrine Glands