* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
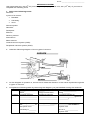
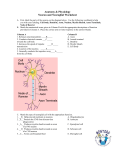
Name: ____________________________ NERVOUS SYSTEM Use pages 322-323, 329 (9 ed.) and the glossary or pages 318-319, 335 (10th ed.) of your text to complete the following work. th 1. Define the following terms: Neurons: 3 parts of a neuron: Dendrite: Cell body: Axon: Nerve impulse: Stimulus: Receptors: Effector: Sensory neuron: Interneuron: Motor neuron: Central nervous system (CNS): Peripheral nervous system (PNS): 2. Label the following diagram of the 3 types of neurons: 3. On the diagram in question 2, use arrows to show the direction of the nerve impulse through the 3 types of neurons. 4. Complete the following table by observing the diagram you just labelled & using the textbook: Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron Structure ______ dendrite Short ______ Function Conduct impulse____ Conducts impulse____ __________________ ___________________ __________________ ___________________ Conduct impulse to _______________ (gland or _________) Location Cell body and dendrite Entirely within _______ are ____________ of ________________ the spinal cord ___________________ _________ are located in spinal cord Cell body in _______ ________________ Axon is _____________ spinal cord ______ dendrite Long or short axon Short _____________ Long _______ Name: ____________________________ 5. Myelin Sheath: a. What is the myelin sheath? b. What is the name of the type of neuroglia cell that makes the myelin sheath? c. What substance makes up the myelin sheath? d. How does the myelin sheath form? e. What are the nodes of Ranvier? f. What part of the neuron is usually wrapped in myelin sheath? The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss from occurring. 6. Neurons are organized into circuits: receptor cells sensory neurons interneuron (CNS) Brain interneuron motor neuron effector cells (muscle or gland) There is another circuit called the reflex arc: Explain the path of a reflex arc (fig. 17.8 p. 329). 7. What is a reflex? 8. Use number to put the following events about the reflex arc in the correct order: ____Impulse causes the muscle to contract ____Impulse reaches interneuron dendrite ____Impulse splits: one axon to brain, one axon to motor neuron dendrite ____Impulse travels along the motor axon ____Impulse travels along the sensory axon ____Impulse travels along the sensory dendrite ____Impulse travels along the motor dendrite ____Stimulus causes and action potential in the sensory receptor