* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons - Manatee School for the Arts
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
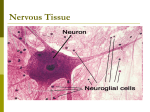
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Part 1: The Nervous System Please watch the following video. - Click the link below. - Adjust volume on speaker (far right on teacher desk). - Increase picture size by clicking bottom right on video. Hit escape to return to ppt https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=OZG8M_ldA 1M Three Functions of the Nervous System: • Sensory Input: afferent pathway (PNS) • Gathers stimuli (receives information) • Integration: (CNS) • Processes and interprets information • Motor Output: efferent • pathway (PNS) • Causes a response to muscles or glands http://www.google.com/imgres? https://www.google.com/search?q=venn+diagram+cns+and+pns&biw=1280&bih=864&tbm=isch&imgil=Nq_SHCt4Jy_p5M%253A%253BmWnM1LxBWHywgM%253 Bhttp%25253A%25252F%25252Fcreately.com%25252Fdiagram%25252Fexample%25252Fi4m3ml2v1%25252Fcns%2525252520vs%2525252520pns&source=iu&pf=m&fir=N q_SHCt4Jy_p5M%253A%252CmWnM1LxBWHywgM%252C_&usg=__2HzuBoSfXTq41d7Bz_LKT2CAC0c%3D&ved=0ahUKEwiPmsbEuq7QAhUDQyYKHTNwBaUQyjcIL http://creately.com/diagram/example/i2529da11/CNS%20and%20PNS Q&ei=cO8sWI-iK4OGmQGz4JWoCg#imgrc=kauTwGTE5RKCvM%3A Organization of the Nervous System: Structural Classification: Functional Classification: • Central Nervous System (CNS): brain & spinal cord • Sensory Division (a.k.a. Afferent): nerves carrying info to the CNS from the body • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): spinal & cranial nerves • Motor Division (a.k.a. Efferent): nerves carrying info from the CNS to the muscles or glands or other nerves • This includes: • Somatic Nervous System: voluntary control (skeletal muscles) • Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): involuntary control (smooth & cardiac). This includes: sympathetic & parasympathetic. Supporting Cells of the Nervous System: 1. Microglial cells: support neurons & carry out phagocytosis 2. Oligodendrocytes: form myelin within the brain; occur in rows along nerve fibers 3. Astrocytes: found between neurons & bv’s; support, regulate [nutrients] & [ions], & form scar tissue following a CNS injury. 4. Ependymal cells: membrane like structure that covers parts of the brain (choroid plexuses) & forms inner linings of brain (ventricles) & spinal cord (central canal). http://www.colorado.edu/kines/Class/IPHY3430-200/image/gila.jpg Neurons: Nerve Cells • Neurons vary in size, shape & function • Mature neurons do NOT divide • All neurons have: • A cell body is the main component of a neuron. It contains cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus, & organelles. • The ER of a cell body is called the chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies (perform protein synthesis). http://www.google.com/imgres? Neuron Anatomy: • Dendrites and axons are nerve fibers that attach to the cell body (most neurons have these). • Dendrites (usually more than 1 on a cell body) are the communication means of one neuron to the next. They receive messages. These are short branched fibers. • Axons take impulses away from the cell body. They are usually one fiber with side branches. • Large axons have a covering sheath called a myelin sheath (a membrane of lipoprotein). • The myelin sheath is composed of Schwann cells (neuroglial cells). • The gaps between the myelin sheaths are called nodes of Ranvier. • In the CNS, white matter are the fibers that are myelinated while gray matter are the fibers that are unmyelinated. http://www.google.com/imgres? A neuron: Terminology: • Nuclei: clusters of cell bodies in the CNS • Nerves: fibers running through the PNS • Ganglia: small clusters of • White Matter: cell bodies in the PNS myelinated fibers (outside the CNS) • Tracts (or nerve tracts): bundles of nerve fibers running through the CNS • Gray Matter: unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies Types of Neurons: Structural Classification: 1. Bipolar neurons: 2 nerve fibers, one at each end (1 axon & 1 dendrite). Found in the nose, eyes, & ears. 2. Unipolar neurons: 1 nerve fiber from the cell body that has 2 branches (1 branch acts as a dendrite & the other branch acts as an axon). 3. Multipolar neurons: many nerve fibers, 1 axon and many dendrites. Found in the brain & spinal cord. http://www.google.com/imgres? Types of Neurons: Functional Classification: 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from peripheral body parts to brain & spinal cord (from PNS to CNS). Most are unipolar, some bipolar. 2. Interneurons: carry impulses between neurons; in CNS. Multipolar neurons. (association neuron) 3. Motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain & spinal cord to the effectors (muscles & glands outside of the NS) to carry out a response. Multipolar. Nerve Impulses: • An unmyelinated nerve fiber carries an impulse slower than a myelinated nerve fiber. • Nerve impulses range in speed according to their diameter (thicker=faster). Ex: skeletal muscle travels ~120 meters/second • Nerve impulses respond in an all-or-none response. • More stimuli= more impulses (per second), not stronger intensity of impulses. Nerve Impulses: • A synapse is a junction between 2 communicating neurons. The neurons are NOT connected. • A synaptic cleft is the gap between these 2 neurons. • A nerve impulse must jump this gap. • A neurotransmitter is a chemical that enables the impulse to jump the synaptic cleft. http://www.google.com/imgres? Neurotransmitters: • There are 2 types: • Excitatory (increase membrane permeability) -impulse will likely occur • Inhibitory (decrease membrane permeability) -impulse will not likely occur • There are at least 50 known neurotransmitters, including these groups: • Acetylcholine (stimulates skeletal muscles) • Monoamimes (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, & serotonin) • Several amino acids • Peptides Reflexes: • These are rapid, involuntary responses • A reflex arc is the simplest nerve pathway that contains only a few neurons. • The withdrawal reflex is a protective reflex (pulling your finger away from a hot pot) b/c it limits tissue damage. In addition to this reflex, interneurons also trigger a response to pain. • Somatic reflexes include skeletal muscles (pulling your hand away from a hot stove). • Autonomic reflexes include smooth and cardiac muscles as well as glands (pupils dilating, mouth ‘watering’) • The knee-jerk reflex is a nerve pathway involving only 2 neurons (1 sensory & 1 motor). Withdrawal Reflex: http://www.mhhe.com/socscience/intro/ibank/ibank/0022.jpg SEE p220-222 in Hole’s textbook https://www.google.com/search?q=reflex+arc&biw=1280&bih=891&tbm=isch&imgil=DUpByfrJ9Q5CRM%253A%253BKwPPSsQ8PtAfpM%253Bhttp%25253A%252 52F%25252Fwww.ib.bioninja.com.au%25252Foptions%25252Foption-e-neurobiology-and-2%25252Fe1-stimulus-andresponse.html&source=iu&pf=m&fir=DUpByfrJ9Q5CRM%253A%252CKwPPSsQ8PtAfpM%252C_&usg=__Jkqx3wBOsUAK4q9MXQ51_9OVSQg%3D&ved=0ahUK EwjLyoLtif3KAhVF7yYKHchxBpcQyjcILQ&ei=YIDDVsuaH8XemwHI45m4CQ#imgrc=-4p3ZSZRNx6coM%3A This slide show was developed by Dana Halloran, Cardinal Mooney High School, Sarasota, FL. Used with her personal permission, adapted and amended by Rosa Whiting, Manatee School for the Arts, Palmetto, FL.