* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
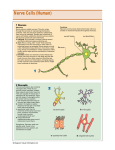
The Nervous system has three major functions: Sensory – monitors internal & external environment through presence of receptors Integration – interpretation of sensory information (information processing) Motor – response to information processed through stimulation of effectors muscle contraction glandular secretion General Organization of the nervous system Two Anatomical Divisions Central nervous system (CNS) ◦ Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) ◦ All the neural tissue outside CNS Afferent division (sensory input) Efferent division (motor output) Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Histology of neural tissue Two types of neural cells in the nervous system: Neurons - For processing, transfer, and storage of information Neuroglia – For support, regulation & protection of neurons Neuroglia (glial cells) CNS neuroglia: • astrocytes • oligodendrocytes • microglia • ependymal cells PNS neuroglia: • Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) • satellite cells Astrocytes • create supportive framework for neurons • create “blood-brain barrier” • monitor & regulate interstitial fluid surrounding neurons • secrete chemicals for embryological neuron formation Oligodendrocytes • create myelin sheath around axons of neurons in the CNS. Myelinated axons transmit impulses faster than unmyelinated axons Microglia • “brain macrophages” • phagocytize cellular wastes & pathogens Ependymal cells • line ventricles of brain & central canal of spinal cord • produce, monitor & help circulate CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) Schwann cells • surround all axons of neurons in the PNS creating a neurilemma around them. Neurilemma allows for potential regeneration of damaged axons • creates myelin sheath around most axons of PNS Satellite cells • support groups of cell bodies of neurons within ganglia of the PNS Neuron structure •Most axons of the nervous system are surrounded by a myelin sheath (myelinated axons) of Ranvier •The presence of myelin speeds up the transmission of action potentials along the axon •Myelin will get laid down in segments (internodes) along the axon, leaving unmyelinated gaps known as “nodes of Ranvier” Key Note Neurons perform all of the communication, information processing, and control functions of the nervous system. Neuroglia outnumber neurons and have functions essential to preserving the physical and biochemical structure of neural tissue and the survival of neurons. Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards the CNS • Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor information from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose tissue) in the periphery of the body • Association (interneurons) – • transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, coordinate outputs • most common type of neuron (20 billion) In order for neural control to occur, “information” must not only be conducted along nerve cells, but must also be transferred from one nerve cell to another across a synapse Most synapses within the nervous system are chemical synapses, & involve the release of a neurotransmitter