* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
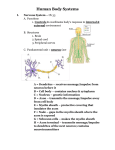
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 35.2 The body’s communication system Controls and coordinates functions throughout the body. Responds to external and internal messages. NEURONS •Specialized cells of the nervous system • Transmit electrical signals called impulses in only one direction. •3 types – sensory neurons-send signals from sensory receptors brain – motor neurons – send signals from the brain muscles & glands – interneurons –carry impulses between sensory & motor neurons NEURON ANATOMY Nucleus Axon terminals Cell body Myelin sheath Nodes Axon Dendrites FUNCTIONS Dendrites – carry impulses from the environment to the cell body Axons – carry impulses away from the cell body Cell body – where the metabolic activity of the cell takes place Myelin sheath – an insulating membrane surrounding the axon NERVE IMPULSE – RESTING NEURON • A nerve impulse is similar to the flow of electrical current through a wire. • When the neuron is NOT sending an impulse, the inside is negative and the outside is positive Na+ and K+ ions move across the cell Membrane via the sodium-potassium pump The Moving impulse An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or the environment Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron The moving impulse An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated strong enough to reach a threshold. The impulse travels rapidly down the axon towards the terminal end. THE SYNAPSE Direction of impulse axon • Where impulses are transferred from one neuron to another. •Chemicals diffuse across a small gap between the cells •Neurotransmitters- are the chemicals that transfer impulses from one neuron to another. •Receptors of the neighboring neuron pick up the chemical message, and a new impulse begins. vesicle Dendrite of Adjacent neuron receptor Axon terminal Neurotransmitter In a fraction of a second after binding to the receptors, the neur0transmitter molecules are released. They are re-absorbed back into the axon terminal Review questions What are the 4 parts of a neuron? What is a threshold? How does a message move from one neuron to another?

























![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)