* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Guided Tour of the Brain
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
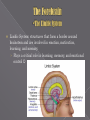
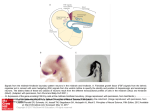
Studying of the Brain The Developing Brain › Neurogenesis The Brainstem › The Hindbrain › The Midbrain The Forebrain › Cerebral Cortex Lobes of the Brain › The Limbic System Structures One early approach to mapping brain functions involved examining the bumps on a person’s skull. Case studies of individuals with brain damage have provided valuable insights into behavior in such area as memory, speech, emotion, movement, and personality. Lesions- surgically altering, removing, or destroying specific portions of the brain › In humans, lesions are produced for medical reasons, such as when part of the brain is surgically altered or removed to relieve uncontrollable seizures Electroencephalograph- allowed scientists to record the brain’s electrical activity through the use of large, diskshaped electrodes placed harmlessly on a person’s scalp By three weeks after conception, a sheet of primal neural cells has formed. This sheet curls to form the hollow neural tube. The neural stem cells divide and multiply, creating specific cells that eventually produce neurons and glial cells. As the neural tube expands, the cavities develop, called the ventricles. During peak periods in the brain development, new neurons are being generated rapidly. Triggered by chemical signals, the new neurons travel to specific locations. For many years, it was thought that the mature brain could lose neurons, but not grow new ones. But new studies showed that the hippocampus, a brain structure that plays a vital role in forming new memories, has the ability to generate new neurons throughout the lifespan. Studies since this discovery have shown that stress, exercise, environmental complexity, and social status have been shown to affect the rate of neurogenesis in rats, birds, and monkeys. But it is unknown if these findings can be applied to the human brain. Includes the hindbrain and midbrain › Located at the base of the brain Hindbrain: › A region at the base of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life functions Midbrain: › The middle and smallest brain region, involved in processing auditory and visual sensory information Connected to the spinal cord with the rest of the brain Made up of three structures › Medulla: Lies directly above the spinal cord; contains centers active in control of breathing, heart rate, and digestion; also controls swallowing, coughing, vomiting, and sneezing › Pons: swelling of tissue; relay information from various other brain regions to the cerebellum › Cerebellum: controls balance, muscle tone, and coordinated muscle movements; affected by alcohol consumption Relay station that contains centers important to the processing of auditory and visual sensory information Process auditory sensations from the left and right ears Helps you visually locate objects and track their movements Substantia nigra: in midbrain; contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons Cerebral Cortex: outer portion of forebrain › Only a quarter an inch thick › Mainly composed of glial cells and neuron cell bodies and axons Gray matter (in reference to color) White matter consists of myelinated axons that connect cerebral cortex to other brain regions › Divided into two cerebral hemispheres connected by corpus callosum Cerebral hemispheres are then divided into four lobes Temporal, occipital, parietal and frontal lobes Temporal Lobe › Contains primary auditory cortex Occipital Lobe › Contains primary visual cortex Parietal Lobe › Involved in somatosensory information (somatosensory cortex) Frontal lobe › Largest lobe › Primary motor cortex › Involved in planning, initiating, and executing voluntary movements Association Areas › Located on all lobes › Combine sensory and motor information › Coordinate interaction among different brain areas Limbic System: structures that form a border around brainstem and are involved in emotion, motivation, learning, and memory. › Plays a critical role in learning, memory, and emotional control Hypothalamus › Regulates behaviors related to survival Eating, drinking, and sexual activity › Often referred to as “the brain within the brain” › Controls secretion of endocrine hormones Influences anterior and posterior pituitary glands Amygdala › Clump of neuron cell bodies at the base of temporal lobe › Involved in emotion and memory