* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the nervous system
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
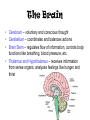
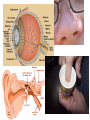
Functions of the Nervous System • Controls and Coordinates functions throughout the body • Responds to internal and external stimuli How does it do it? • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath Neurons 3 Main Types: Sensory neurons – carry messages from sense organs to the spinal cord and brain Motor neurons – carry messages from the brain to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons Sending Messages • An impulse begins when it is stimulated either by another neuron or the environment • The impulse is sent through many neurons and cells • The space between the cells is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help the impulse cross over the synapse Parts of the Nervous System • The Central Nervous System: – Relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information – Includes the brain and spinal cord • The Peripheral Nervous System: – Sensory Division: transmits impulses from sense organs – Motor Division: transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands The Brain • Cerebrum – voluntary and conscious thought • Cerebellum – coordinates and balances actions • Brain Stem – regulates flow of information, controls body functions like breathing, blood pressure, etc. • Thalamus and Hypothalamus – receives information from sense organs, analyzes feelings like hunger and thirst The Spinal Cord • Connects the brain to the rest of the body – Acts like a telephone line sending a message • Controls simple reflexes (like sneezing and blinking) The Senses • Special neurons, called sensory receptors, react to specific stimuli like light or sound • The five major types of sensory receptors are: Sense damaged cells – Pain Receptors Changes in temperature – Thermoreceptors – Mechanoreceptors Pressure, touch, sound, motion Chemical Changes – Chemoreceptors Light – Photoreceptors Where are these receptors found?