* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
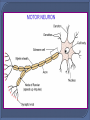
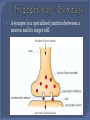
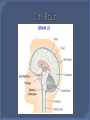
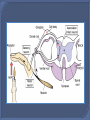
The Nervous System The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of the brain and spinal cord. The cranial nerves, spinal nerves and ganglia make up the PNS. The cranial nerves connect to the brain. The cranial and spinal nerves contain the axons (fibres) of sensory and motor nerve cells. Nerve cells are also known as neurons. Sensory Neurons Sensory neurons carry electrical signals (impulses) from receptors or sense organs to the CNS. Sensory neurons are also called afferent neurons. The cell body of sensory neurons is outside the CNS in ganglia. Motor Neurons Motor neurons carry impulses from the CNS to effector organs. Motor neurons are also called efferent neurons. The cell bodies of motor neurons are inside the CNS. A synapse is a specialised junction between a neuron and its target cell. Cerebrum: centre for sensory and motor control, language, memory, intelligence, and consciousness. Cerebellum: muscle co-ordination, movement and balance. Medulla Oblongata: controls breathing and heart rate. Hypothalamus: osmoregulation and temperature control. Pituitary Gland: secretes a wide variety of hormones – a major endocrine gland. A reflex action is a very fast unconscious response to an unexpected and potentially dangerous stimulus. Examples of reflex action: knee jerk, eye blink, pupil size alteration, closure of the glottis on swallowing. A reflex arc is a specific nerve pathway involved in a fast, unconscious response to an unexpected stimulus. E.g. Spinal Reflex Action - the withdrawal of hand when finger jabbed unexpectedly with a pin. Pain and pressure receptors in the skin are stimulated. Sensory neurons carry the impulses to the spinal cord by way of the dorsal root. An interneuron picks up the impulse from the sensory and transmits it to the motor neuron. At the same time the impulse is also transmitted to the brain. The motor neuron stimulates the specific effector organ to make the appropriate response, muscles in the arm are stimulated to contract pulling the hand away from the pin. The response is very fact – occur before the brain is aware of the situation. The brain, having received the information, may transmit impulses to other muscles to modify the response.