* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
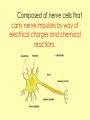
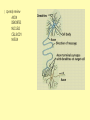
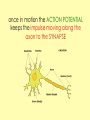
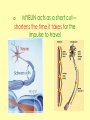
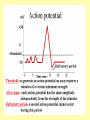
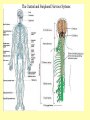
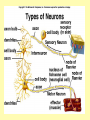
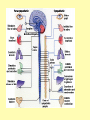
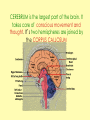
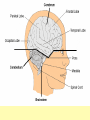
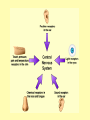
Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM – Regulates all body activities, learning and memory. Composed of nerve cells that carry nerve impulses by way of electrical charges and chemical reactions. Ultimate coordinator of homeostasis. · speedy review AXON DENDRITES NUCLEUS CELL BODY MYELIN Nerve impulse Travels via electrical current. RESTING POTENTIAL no impulse being conducted once in motion the ACTION POTENTIAL keeps the impulse moving along the axon to the SYNAPSE The synapse is the space between the terminal end of one Neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron. at the synapse NEUROTRANSMITTERS carry the signal to the next neuron, muscle, etc. o MYELIN acts as a short cut— shortens the time it takes for the impulse to travel Central Nervous System brain & spinal cord Peripheral Nervous system everything else nerves and ganglia that lie outside the CNS. (spinal nerves, cranial nerves, ganglia, motor and sensory neurons.) Sensory Neuron Pick up sensory information from the sense organs and relay the information to the interneurons.( brain and spinal cord) Interneuron Relay information from sensory neurons to motor neurons . Motor Neuron Stimulate muscles or glands in effector organs to cause a response. Two Types of Motor Neurons Somatic - voluntary - skeletal muscles Autonomic - involuntary - smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glands Autonomic Nervous system Sympathetic - Fight or flight Parasympathetic - sleep or snack Structures in the CNS- Brain and spinal cord CEREBRUM is the largest part of the brain. It takes care of conscious movement and thought. It’s two hemispheres are joined by the CORPUS CALLOSUM WRINKLES provide more surface area Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body o CEREBELLUM is found below and to the back of the cerebrum. It coordinates commands from the cerebrum. This action is involuntary o THALAMUS & HYPOTHALAMUS Relays sensory input to The right places in cerebrum Maintains homeostasis (hunger, thirst, body temp, sleep, H20 balance, blood pressure) o BRAINSTEM position is self explanatory. Coordinates and serves as port for coming/going info.; regulates heart rate and respiration. o SPINAL CORD links the brain and PNS. It also stimulates reflexes Organization of the PNS—starts with two major divisions Sensory (incoming info) Motor (outgoing info) Somatic (voluntary) Autonomic (involuntary) Sympathetic Parasympathetic SPEEDY REVIEW Structures of PNS SENSORY NEURON ~ senses stimulus and alerts CNS Gets its info from a RECEPTOR ORGAN INTERNEURON ~ w/i CNS, tells brain what’s going on MOTOR NEURON ~ takes info from CNS and initiates a reaction in the EFFECTOR ORGANS GANGLIA ~ a group of neural cell bodies that is found outside of the CNS (w/i the PNS) Receptor organs make up all our senses (excepting ESP) Sight—eyes, rods and cones Hearing & balance—ears, eardrums & bones & and semicircular canals Smell—nose, olfactory nerves Taste—tongue, taste buds Touch (heat/cold, pressure, pain)—receptors in skin