* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nervous system
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
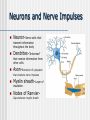
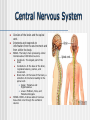
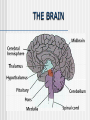
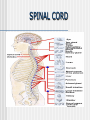
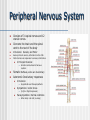
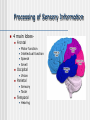
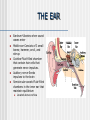
NERVOUS SYSTEM Science, Technology, & Society MR. CANOVA Period 11 Neurons and Nerve Impulses Neuron-Nerve cells that transmit information throughout the body Dendrites-”Antennae” that receive information from other cells Axon-Extension of cytoplasm that conducts nerve impulses Myelin sheath-Layer of insulation Nodes of RanvierGaps between myelin sheath Neuron Function Membrane potential- The difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane. Expressed in voltage. Resting potential- The membrane potential of a neuron at rest -70 millivolts (mV) Inside of cell is negatively charged, outside of cell is positively charged K+ ions in the cell, Na+ out of the cell Action potential- A nerve impulse Approaches +40 millivolts (mV) Inside of cell is positively charged, outside of cell is negatively charged Na+ ions in the cell, K+ out of the cell Communication between Neurons Synapse: Neurotransmitters: The junction where a neuron meets another cell • Pre/Post synaptic cell Signal molecules that bind to receptor proteins on the postsynaptic cleft and interact wit the postsynaptic cell • Can excite or inhibit the activity of a cell it binds to Membrane potential: + ions enter neuron, an action potential is produced (excitation) - ions enter neuron, an action potential is suppressed (inhibition) Central Nervous System Consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Interprets and responds to information from the environment and from within the body. BRAIN- The body’s main processing center. Contains about 100 billion neurons. Cerebrum- The largest part of the brain Cerebellum- At the base of the brain, regulates balance, posture, and movement. Brain stem- At the base of the brain, a collection of structures leading to the spinal cord. • Upper- Thalamus and Hypothalamus • Lower- Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla oblongata SPINAL CORD- A dense cable of nervous tissue that runs through the vertebral column. THE BRAIN SPINAL CORD Peripheral Nervous System Consists of 31 spinal nerves and 12 cranial nerves. Connects the brain and the spinal cord to the rest of the body 2 Divisions: Sensory and Motor Sensory-Directs sensory information to the CNS Motor-Carries out responses to sensory information. 2 Principal Divisions: • Somatic and Autonomic Nervous systems Somatic-Reflexes, some are involuntary Autonomic-Involuntary responses 2 Divisions: • Sympathetic- Under stress • Sympathetic and Parasympathetic (Fight or Flight responses) Parasympathetic- Normal conditions • When body is at rest (ie-sleep) SENSORY RECEPTORS Receptor type Stimuli Locations Thermoreceptors Temperature change Skin, Hypothalamus Pain receptors Tissue damage Tissues and Organs Mechanoreceptors Movement, Pressure, Tension Skin, Ears, Muscles Photoreceptors Light Eyes Chemoreceptors Chemical Tongue, Nose Processing of Sensory Information 4 main lobes Frontal • • • • Motor function Intellectual function Speech Smell Occipital • Vision Parietal • Sensory • Taste Temporal • Hearing THE EYE Pupil-Allows light to enter the eye Lens-Disk that focuses light onto retina Retina-Lining on back of the eye that converts light energy into electrical signals Cornea-Transparent covering on eye Iris-Controls amount of light that enters the eye Rods-Respond to dim light Cones-Respond to bright light and allow color vision Optic nerve-Exits back of the eye and runs along base of the brain to the thalamus THE EAR Eardrum-Vibrates when sound waves enter Middle ear-Consists of 3 small bones; hammer, anvil, and stirrup Cochlea-Fluid-filled chamber that contain hair cells that generate nerve impulses. Auditory nerve-Sends impulses to the brain Semicircular canals-Fluid-filled chambers in the inner ear that maintain equilibrium Located above cochlea CHEMICAL SENSES CHEMORECEPTORS LOCATED ON THE TONGUE • 4 CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES OLFACTORY RECEPTORS LOCATED IN THE NASAL PASSAGE • Sense of smell Drugs and the Nervous System Drug Examples Psychoactive effects Depressants Alcohol, Sedatives Decreased CNS activity Stimulants Cocaine, Crack, Nicotine Increased CNS activity Inhalants Paint thinner, Glue Disorientation, Confusion Hallucinogens LSD, PCP, MDMA Anxiety, Hallucinations THC Marijuana, hashish Short-term memory loss Narcotics Heroin, Morphine, Codeine, Opium Sedation Drug Addiction and Neuron Function Addiction- Physiological response caused by use of a drug that alters the normal functioning of neurons and synapses. Tolerance- Increasing amounts of the drug are needed to achieve the desired sensation. Withdrawal- Emotional and physical symptoms caused by removal of the drug from the body. Depressant- Drug that decreases the activity of the CNS Stimulant- Drug that increases the activity of the CNS