* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
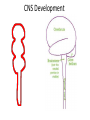
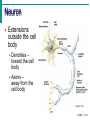
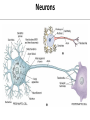
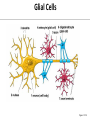
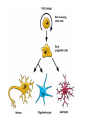
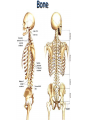
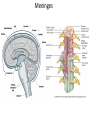
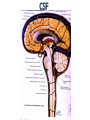
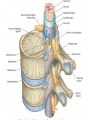
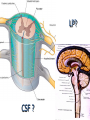
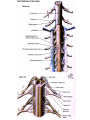
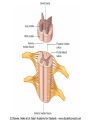
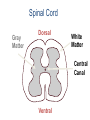
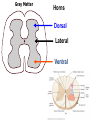
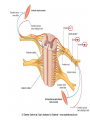
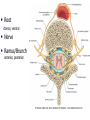
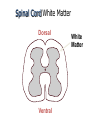
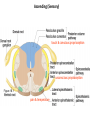
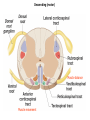
Nervous System Some Interesting Facts • 85 billion (85,000,000,000) neurons in the human brain. • 3,000 years one cell/second • 1 neuron cell body = 10 microns wide 85,000,000,000 neurons = 850 km • If you use a basketball (diameter = ~24 cm) as the cell body, then your axon would have to be 240,000 cm (2.4 kilometers) in length! ► A baby's brain is a mystery. ► The mystery begins in the womb -- only four weeks into gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connections between cells. ► Every cell is precisely in its place, every link between neurons carefully organized. Nothing is random, nothing by chance. CNS Development Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input changes = stimuli 2. Integration processing 3. Motor output response to stimuli (The response activates muscles or glands) Neuron Extensions outside the cell body Dendrites – toward the cell body Axons – away from the cell body Figure 7.4a Slide 7.10 Neurons Glial Cells Figure 12.2b Anatomy of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Nerve outside the brain and spinal cord Slide 7.2 Central nervous system (CNS) – Brain – Spinal cord CNS is protected by • Bone • Meninges • CSF Bone Meninges CSF Spinal cord LP? CSF ? Structure of spinal cord • Roots dorsal, ventral • Horns anterior, posterior, lateral • Columns anterior, posterior, lateral Spinal Cord Gray Matter Dorsal White Matter Central Canal Ventral Gray Matter Horns Dorsal Lateral Ventral v v • Root dorsal, ventral • Nerve • Ramus/Brunch anterior, posterior Spinal Cord White Matter Dorsal Ventral White Matter Ascending (Sensory) touch & conscious proprioception unconscious proprioception Figure 16.1 pain & temperature Descending (motor) Muscle balance Muscle movement Brain