* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CNS
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
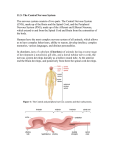
Central Nervous System CNS • Communication and control centre of body • Brain and spinal cord Nerve Cells • Neuron- basic structural and functional unit of nervous system • Vary in size and shape • All consist of dendrite, cell body and axon CNS- Cell Body • Contains nucleus and cytoplasm • Cytoplasm similar to other cells CNS- Dendrites • Short extensions of cytoplasm • Carry nerve impulse INTO cell body CNS- Axon • • • • Long extension from cell body Usually carry impulse away from cell body Length highly varied Most myelinated- covered by fatty material called myelin CNS • Interneurons- brain and spinal cord • Many branches able to send and receive messages from adjacent neurons • Grey Matter- nerve cell bodies and unmyelinated fibres • White matter- myelinated fibres Generalised Neuron Protecting the CNS • Bone • Meninges • CSF- protection, support and trasnport Brain- Cerebrum • Biggest part of brain • Cerebral cortex- Outer surface of grey matter, 2- 4 mm thick • Below cortex is basal ganglia • Right and left hemisphere • Highly convoluted Brain- Cerebrum Brain- Cerebrum • 4 lobes- frontal, temporal, occipital and parietal Brain- Cerebrum • Tract- bundles of nerve fibers • Connect various areas of cortex within the same hemisphere • Carry impulses between the left and right hemisphere • Connect cortex to other parts of brain or spinal cord Brain- Cerebrum: Function • Cortex- thinking, reasoning, learning, memory, intelligence, sense of responsible, perception of senses, initiation and control of voluntary muscle contractions. Brain- Cerebrum: Function • Sensory- interpret impulses from receptors • Motor- control muscular movement • Association- intellectual and emotional areas Brain- Cerebellum • • • • • Under rear part of cerebrum 2nd largest part of brain Folded into parallel ridges Outer- grey Inner- white- branches to all parts of cerebellum Brain- Cerebellum: Function • Posture, balance, coordination • Receives info from inner ear and stretch receptors in skeletal muscles • Unconsciously controls us- jerky without it Hypothalamus • Middle of brain • Mostly concerned with homoestasis Brain- Hypothalamus: Function • Regulation of – ANS- HR, BP, secretion of digestive juices, alimentary canal, pupil dialation – Body temp – Food and water intake – Patterns of walking and sleeping – Conc urinary bladder – Emotional responses – HORMONES!! Brain- Medulla Oblongata • Continuation of spinal cord • 3cm long • Extends just above point where spinal cord enters scull • ‘Highway for nerves’ Brain- Medulla Oblongata: function • • • • • Cardiac centre Respiratory centre Vasomotor center Swallowing, sneezing, coughing and vomiting Controlled by higher centers in brain Spinal Cord • Roughly cylindrical • Foramen magnum to L2 • Heavily protected – Vertebral canal – Meningies • Outer layer not connected to bone rather space filled with fat, connective tissue and blood serving as padding for when spine is bent Spinal Cord • Grey and white matter opposite configuration to brain Spinal Cord • Central Canal- CSF • Ascending and Descending Tracts – Bundles of myelinated nerve fibre Structure Function Cerebral cortex Higher order functions such as thinking, reasoning, memory, learning, conscious awareness of surroundings Cerebellum Coordination of fine contraction so muscles resulting in smooth movements and the maintenance of posture and balance Hypothalamus Homeostasis. Regulation of hear, digestive system, appetite, thirst, metabolism, body temp, response to fear or anger Medulla oblongata Under influence of the hypothalamus regulates the hear, breathing and diameter of blood vessels Spinal Cord Provides a pathway for communication between muscles and gland and the brain. Integration of automatic, protective reflexes Control of Movement • Cerebral Cortex – Motor Association Area of Brain initiates intention to move – Neurons make up program for sequence and intensity of contractions – Program then sent to Primary motor area (primary motor cortex) – Impulses then sent to lower centres in brain and spinal cord- result being contraction Motor Homunculus Homunculus “A diagram of the body that shows the relative size of parts of the cortex devoted to control of different muscles.” Cross overs Cerebellum • Receive nerve impulses from cerebrum through upper motor neurons • Also receives information from eyes, ears and stretch receptors • Smoothes contractions • Learning of motor skills • Maintain Balance