* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
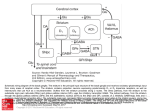
The basal ganglia in Parkinson disease. The primary defect is destruction of the dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc. The striatal neurons that form the direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differential effect on the two outflow pathways; the direct pathway to the SNpr and GPi is less active (structures in purple), whereas the activity in the indirect pathway is increased (structures in red). The net effect is that neurons in the SNpr and GPi become more active. This leads to increased inhibition of the VA/VL thalamus and reduced excitatory input to the cortex. Light blue lines indicate primary pathways with reduced activity. (See legend to Figure 22–2 for Source: Treatment of Central Nervous System Degenerative Disorders, Goodman & Gilman's: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12e definitions of anatomical abbreviations.) Citation: Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC. Goodman & Gilman's: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12e; 2011 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 11, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved