* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
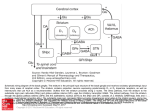
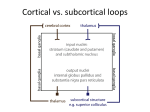
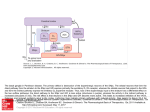
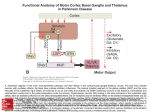
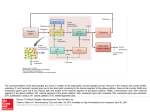
Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as interneurons that use ACh as a neurotransmitter. Outflow from the striatum proceeds along 2 routes. The direct pathway, from the striatum to the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) and globus pallidus interna (GPi), uses the inhibitory transmitter GABA. The indirect pathway, from the striatum through the globus pallidus externa (GPe) and the subthalamic nucleus (STN) to the SNpr and GPi, consists of 2 inhibitory GABA-ergic links and 1 excitatory glutamatergic projection (Glu). The substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) provides dopaminergic innervation to the striatal neurons, giving rise Source: Treatment of Central Nervous System Degenerative Disorders, Goodman and Gilman's Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2e to both the direct and indirect pathways, and regulates the relative activity of these 2 paths. The SNpr and GPi are the output structures of the basal Citation:feedback Hilal-Dandan Bruntoncortex LL. Goodman andventroanterior Gilman's Manual of Pharmacology and 2e; 2016 Available at: ganglia and provide to theR, cerebral through the and ventrolateral nuclei of Therapeutics, the thalamus (VA/VL). http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 03, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved