A Critical Review of Secondary Neurodegeneration
... Another approach used to study accumulation of amyloid-β in non-invasive imaging studies is the Pittsburgh compound B (PiB). [11C]PiB (PiB is labelled with radioactive carbon 11) is injected intravenously and is then used in combination with positron emission tomography (PET) to detect cerebral amyl ...
... Another approach used to study accumulation of amyloid-β in non-invasive imaging studies is the Pittsburgh compound B (PiB). [11C]PiB (PiB is labelled with radioactive carbon 11) is injected intravenously and is then used in combination with positron emission tomography (PET) to detect cerebral amyl ...
The thalamus as a putative biomarker in neurodegenerative disorders
... either drivers or modulators; this classification is regardless of whether the fibres originate from cortical or subcortical structures (see Figure 3). Afferent fibres can be defined on the basis of their synaptic morphology (e.g., drivers have large terminals on proximal dendrites forming multiple ...
... either drivers or modulators; this classification is regardless of whether the fibres originate from cortical or subcortical structures (see Figure 3). Afferent fibres can be defined on the basis of their synaptic morphology (e.g., drivers have large terminals on proximal dendrites forming multiple ...
Lec: 1 Dr.Methaq Mueen Hemodynamic disorders Hemo means
... edema of the affected limb. *Generalized increase in venous pressure with systemic edema occur in congestive heart failure in which reduced cardiac output causes reduced renal perfusion & trigger of rennin angiotensin aldosterone axis causing sodium & water retention by kidney in order to increase i ...
... edema of the affected limb. *Generalized increase in venous pressure with systemic edema occur in congestive heart failure in which reduced cardiac output causes reduced renal perfusion & trigger of rennin angiotensin aldosterone axis causing sodium & water retention by kidney in order to increase i ...
A computational model of action selection in the basal ganglia. I. A
... explanation of the functional contribution to selection made by dierent basal ganglia nuclei. Fourth, given the importance of dopamine in regulating basal ganglia function (see for example Mink 1996), to begin an analysis of the role of dopamine in the context of selection. This paper deals primari ...
... explanation of the functional contribution to selection made by dierent basal ganglia nuclei. Fourth, given the importance of dopamine in regulating basal ganglia function (see for example Mink 1996), to begin an analysis of the role of dopamine in the context of selection. This paper deals primari ...
Chapter 122: Neurocircuitry Of Parkinson`s Disease
... shown that these neurons are different from corticospinal projection neurons (20,295) and tend to have slower conduction velocities and lower spontaneous rates, and are usually not responding to somatosensory input. According to the current model of the functions of the basal ganglia–thalamocortical ...
... shown that these neurons are different from corticospinal projection neurons (20,295) and tend to have slower conduction velocities and lower spontaneous rates, and are usually not responding to somatosensory input. According to the current model of the functions of the basal ganglia–thalamocortical ...
PDF of this article
... circuitry. As repeatedly demonstrated by experimental studies, the subthalamic nucleus can modulate the neuronal activity of both basal ganglia output nuclei (4-6). In addition, recent studies have shown that the subthalamic nucleus receives direct excitatory projections from the primary motor corte ...
... circuitry. As repeatedly demonstrated by experimental studies, the subthalamic nucleus can modulate the neuronal activity of both basal ganglia output nuclei (4-6). In addition, recent studies have shown that the subthalamic nucleus receives direct excitatory projections from the primary motor corte ...
Medial medullary syndrome
... • MS is the most common chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease affecting the central nervous system. • MRI criteria for diagnosis of MS in patients with clinical syndrome suggestive of MS include demonstration of disease dissemination in time and space. • Active lesions may demonstrate diffusio ...
... • MS is the most common chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease affecting the central nervous system. • MRI criteria for diagnosis of MS in patients with clinical syndrome suggestive of MS include demonstration of disease dissemination in time and space. • Active lesions may demonstrate diffusio ...
Frontotemporal Dementia and Mania - University of California, San
... case of new-onset mania, this is particularly important in the elderly. Older patients with new-onset mania are more than twice as likely to suffer from a comorbid neurological disorder (3), including silent cerebral infarcts (65% in newonset versus 25% in chronic illness) (4). In addition to a stan ...
... case of new-onset mania, this is particularly important in the elderly. Older patients with new-onset mania are more than twice as likely to suffer from a comorbid neurological disorder (3), including silent cerebral infarcts (65% in newonset versus 25% in chronic illness) (4). In addition to a stan ...
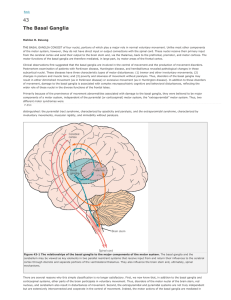
The Basal Ganglia and Motor Control
... movements is dependent upon the exact timing in the activation and switching of motor programs that have been imprinted in the brain during the course of motor learning processes (motor memory). In daily life, once a movement has been initiated, the execution of most of our willed, intentional movem ...
... movements is dependent upon the exact timing in the activation and switching of motor programs that have been imprinted in the brain during the course of motor learning processes (motor memory). In daily life, once a movement has been initiated, the execution of most of our willed, intentional movem ...
Neuropathological Alterations in Alzheimer Disease
... or synaptic loss. This plaque type is not considered for the pathological diagnosis of AD because it is a relatively common finding in the brain of cognitively intact elderly people. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA): deposits of amyloid b in the tunica media of leptomeningeal arteries and cortical ...
... or synaptic loss. This plaque type is not considered for the pathological diagnosis of AD because it is a relatively common finding in the brain of cognitively intact elderly people. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA): deposits of amyloid b in the tunica media of leptomeningeal arteries and cortical ...
Subcortical loops through the basal ganglia
... a range of debilitating clinical conditions whose most obvious manifestations are disturbances in movement. It is increasingly recognized, however, that many of these disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s chorea, schizophrenia, attention deficit disorder, Tourette’s syndrome and var ...
... a range of debilitating clinical conditions whose most obvious manifestations are disturbances in movement. It is increasingly recognized, however, that many of these disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s chorea, schizophrenia, attention deficit disorder, Tourette’s syndrome and var ...
Basal Ganglia - Adaptive Behaviour Research Group
... Lying either side of the forebrain/midbrain boundary, at the hub of the mammalian brain, the basal ganglia are a group of highly interconnected brain structures with a critical influence over movement and cognition. The importance of these nuclei for a cluster of human brain disorders including Park ...
... Lying either side of the forebrain/midbrain boundary, at the hub of the mammalian brain, the basal ganglia are a group of highly interconnected brain structures with a critical influence over movement and cognition. The importance of these nuclei for a cluster of human brain disorders including Park ...
Update on models of basal ganglia function and dysfunction
... importance of dopamine release at regulating the transmission at specific synapses in the striatum are accepted. However, some of the details of the earlier pathophysiology models of basal ganglia diseases have fallen by the wayside, most likely because the anatomical models were too rigidly transfor ...
... importance of dopamine release at regulating the transmission at specific synapses in the striatum are accepted. However, some of the details of the earlier pathophysiology models of basal ganglia diseases have fallen by the wayside, most likely because the anatomical models were too rigidly transfor ...
BRAIN - ESPN.com
... Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury can trigger the development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive neurodegeneration characterized by the widespread deposition of hyperphosphorylated tau (p-tau) as neurofibrillary tangles (Corsellis and Brierley, 1959; Corsellis et al., 1973 ...
... Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury can trigger the development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive neurodegeneration characterized by the widespread deposition of hyperphosphorylated tau (p-tau) as neurofibrillary tangles (Corsellis and Brierley, 1959; Corsellis et al., 1973 ...
differential diagnosis of corpus callosum lesions
... • The corpus callosum has a rich blood supply from the anterior communicating artery which supplies the genu, the pericallosal artery which supplies the body, and the posterior pericallosal artery, a branch of the posterior cerebral artery, which feeds the splenium, thus infarcts are rare and usuall ...
... • The corpus callosum has a rich blood supply from the anterior communicating artery which supplies the genu, the pericallosal artery which supplies the body, and the posterior pericallosal artery, a branch of the posterior cerebral artery, which feeds the splenium, thus infarcts are rare and usuall ...
Cerebral amyloidosis, amyloid angiopathy, and their relationship to
... intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) and reactive gliosis, and the loss of presynaptic terminals and neuronal subpopulations in well defined brain areas. At autopsy, senile plaques and NFT chiefly define the disease whereas other pathological features are often ignored or regarded as coincide ...
... intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) and reactive gliosis, and the loss of presynaptic terminals and neuronal subpopulations in well defined brain areas. At autopsy, senile plaques and NFT chiefly define the disease whereas other pathological features are often ignored or regarded as coincide ...
Basal Ganglia: Mechanisms for Action Selection
... representing each of those actions. A long-standing concept in basal ganglia research is the existence of parallel loops running through the basal ganglia (Alexander et al. 1986; Middleton and Strick 2000). At the macroscopic level, independent domains of the basal ganglia have been identified by th ...
... representing each of those actions. A long-standing concept in basal ganglia research is the existence of parallel loops running through the basal ganglia (Alexander et al. 1986; Middleton and Strick 2000). At the macroscopic level, independent domains of the basal ganglia have been identified by th ...
Basal Ganglia objectives - NBio401
... -Be able to explain how, in addition to the pathways affecting limb movements, there are other loops between the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex that perform analogous functions for oculomotor, executive, and emotional systems. - Be able to describe the type of learning in which the basal ganglia ...
... -Be able to explain how, in addition to the pathways affecting limb movements, there are other loops between the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex that perform analogous functions for oculomotor, executive, and emotional systems. - Be able to describe the type of learning in which the basal ganglia ...
Convergent grey and white matter evidence of
... Introduction Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a common cause of young onset dementia (565 years) after Alzheimer’s disease (Ratnavalli et al., 2002). Clinical diagnostic criteria have been proposed (Neary et al., 1998), but the differentiation from other dementias remains difficult with standard neu ...
... Introduction Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a common cause of young onset dementia (565 years) after Alzheimer’s disease (Ratnavalli et al., 2002). Clinical diagnostic criteria have been proposed (Neary et al., 1998), but the differentiation from other dementias remains difficult with standard neu ...
CEREBRAL CORTEX - Global Anatomy Home Page
... areas that are closely associated with a particular sensory modality or motor cortex, but whose functions are clearly more complex and “global” in nature than the primary areas. Most of what is presently known about the function of association areas is derived from the effects of lesions. Functions ...
... areas that are closely associated with a particular sensory modality or motor cortex, but whose functions are clearly more complex and “global” in nature than the primary areas. Most of what is presently known about the function of association areas is derived from the effects of lesions. Functions ...
The Basal Ganglia - The Brain from Top to Bottom
... The globus pallidus is itself divided into medial and lateral portions. This is by the medial medullary lamina. The globus pallidus has a distinctive pale appearance (i.e., dark appearance in myelin-stained sections) due to the large numbers of myelinated fibres that traverse it, terminate in it and ...
... The globus pallidus is itself divided into medial and lateral portions. This is by the medial medullary lamina. The globus pallidus has a distinctive pale appearance (i.e., dark appearance in myelin-stained sections) due to the large numbers of myelinated fibres that traverse it, terminate in it and ...
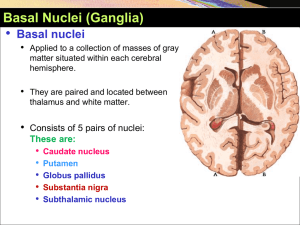
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
... Function of Basal Nuclei Basically the activity of basal nuclei begins by information received from sensory cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra, and red nucleus, according to thoughts of mind. • These information is integrated within corpus striatum and channeled within globus pallidus and outflow b ...
Functional Anatomy, Physiology and Clinical Aspects of Basal Ganglia
... The evidence of the anatomical and physiological brain research supported by clinical data and theoretical models suggests there are at least five loops (also called circuits) related to motor, emotional and cognitive functioning control (Alexander et all., 1986; DeLong et all., 1998). The loops div ...
... The evidence of the anatomical and physiological brain research supported by clinical data and theoretical models suggests there are at least five loops (also called circuits) related to motor, emotional and cognitive functioning control (Alexander et all., 1986; DeLong et all., 1998). The loops div ...
Periosteum - Maryville University
... Periosteum • Central nervous system is protected by the bone structure (skull and vertebral column) as well as meninges. Meninges include dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater. These layers are continuous linings in both spinal cord and brain. • Periosteum, consists of collagenous connective tissue a ...
... Periosteum • Central nervous system is protected by the bone structure (skull and vertebral column) as well as meninges. Meninges include dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater. These layers are continuous linings in both spinal cord and brain. • Periosteum, consists of collagenous connective tissue a ...
Principles of Neural Science
... highly organized connections with virtually the entire cerebral cortex, as well as the hippocampus and amygdala. Finally, a wide range of motor and nonmotor behaviors have been correlated with activity in individual basal ganglia neurons in experimental animals and with metabolic activity in the bas ...
... highly organized connections with virtually the entire cerebral cortex, as well as the hippocampus and amygdala. Finally, a wide range of motor and nonmotor behaviors have been correlated with activity in individual basal ganglia neurons in experimental animals and with metabolic activity in the bas ...