* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT File - Newark Central Schools
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
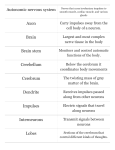
NERVOUS SYSTEM Essential question: What are the differences between responses with the nervous system versus responses with the endocrine system? In humans, as in other animals, regulation is achieved by the integration of the nervous and the endocrine system. The nervous and endocrine systems if humans show certain similarities and certain differences. Similarities: •Both secrete chemical messengers. •The nervous system secretes neurotransmitters and the endocrine system secretes hormones. Both play a major role in homeostasis. Differences: ► ► ► Nerve responses are more rapid than the endocrine responses. Nerve responses are shorter in duration than endocrine responses. Nerve responses travel through the nervous system and endocrine responses travel through the circulatory (blood) system. Essential questions: What are the three types of neurons? What is the function and location of each type? Functional Organization: • • The neuron is the basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system. The nervous system is composed of three different neurons. The Three Types of Neurons: • Sensory neuron • Interneuron • Motor neuron Neurons Sensory neuron-transmits impulses from receptors to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Receptors-Sense organs where sensory neurons are concentrated. Exs. Eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Interneurons: Located mainly in the CNS (brain and spinal cord). Interprets impulses (messages). Relays impulses to motor neutrons. Motor neurons: transmits impulses from the CNS to effectors Effector:. A cell, tissue, or organ, which produces a response to a stimulus. Exs. Muscles and glands Essential Question: What is a nerve? Nerves: bundles of neurons that are specialized for long distances and highspeed impulse transmission. Ex. Optic nerve Optic Nerve Sciatic Nerve Parts of a Neuron: Essential questions: What are the parts of a neuron? What is the function of each of these parts? Parts of a Neuron: Every neuron is composed of: •Dendrites •Cyton (cell body) •Axon •Terminal branches (end branches) Dendrites: • Receive impulses. • Carries impulses towards the cyton. Axon: • Carries impulses away from the cyton. • Protected with a myelin sheath Essential question: How are impulses transmitted from one neuron to the next? Impulse Transmission: Essential Questions: What is a synapse? What is the relationship between a synapse and a neurotransmitter? Synapse-space between two neurons. Neurotransmitters: ► Chemical released by terminal branches of one neuron. ► Starts a new impulse in next neuron. ► 30 different known neurotransmitters. Exs. Acetylcholine, norepinephrine Nerve Transmission Nerve Transmission Essential question: What are the parts and functions of the brain? The Brain • • • • • • The brain weight approximately 1.5 kg, but uses 25 % of the body’s oxygen supply. It is composed of billions of interconnecting neurons. The brain is protected by 3 membranes (Meninges) and fluid. The brain is composed of three main parts: Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla Parts of the Brain Cerebrum: • • • • • • • • • Largest part of the brain. Composed of two halves (hemispheres). Contains many convolutions (folds). Functions include: Controls voluntary movement (skeletal). Intelligence Memory Speech and language Senses Cerebellum and Medulla Located in the back portion of the brain. Functions include: Balance Posture Coordination Medulla: Located at the top of the spinal cord. Functions include: Controls and coordinates involuntary activity. Exs. Breathing, heart rate, peristalsis, and blood pressure Essential Questions: What is the CNS? What is structures make up the CNS? The CNS is composed of the brain and the spinal cord. Spinal Cord: a. Protected by vertebrae of the spinal column b. Relays impulses to and from the brain. c. Controls certain reflexes. Essential Questions: What is the PNS? What is a reflex arc? How does a reflex arc help to maintain homeostasis? Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) a. Located outside of the CNS. b. Made up of all of the neurons and nerve fibers outside the brain and spinal cord. Reflex Arc Essential question: What are some diseases that are associated with the nervous system? Diseases of the Nervous System: Cerebral Palsy: • Name for a collective group of disorders that affect a person’s control of motor functions. • Caused by brain damage just before of after birth. What do these three men have in common? Multiple Sclerosis • • • Destruction of the myelin sheath. Symptoms include shaking of hands, blurred vision, and slurred speech. May appear and disappear for years. Alzheimer’s Disease: Cause unknown. Progressive, degenerative disease. Eventual memory lost, inability to think, speak, or care for oneself. Usually fatal. Parkinson's Strikes Again!!! Parkinson’s disease: ► ► ► ► ► Cause unknown. Neurons can no longer produce the neurotransmitter-dopamine. Symptoms include: tremors, poor balance, lack of coordination, stiffening of muscles. One million people in the us have Parkinson’s and 600,000 people are diagnosis with it annually. On set is usually over the age of 60. The Many Faces of Parkinson’s