* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The human brain - "G. Galilei" – Pescara
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
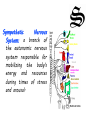
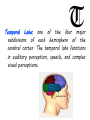
The human brain Atkins Peter 1940- Chemist Acetylcholine : a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in attention, learning, and memory. Amygdala : a part of the limbic system always alert to threats. Axon : the long branch of a nerve cell that transmits information to other cells. Anterior commissure : is a bundle of nerve fibers (white matter) of nerve cells connecting the two cerebral hemispheres. Bell Alexander 1847/1922 Scientist, engineer Brain : the part of the central nervous system enclosed in the cranium of humans and other vertebrates, consisting of a soft, convoluted mass of grey and white matter and serving to control and coordinate the mental and physical actions. Brainstem : is the posterior part of the brain which includes the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. Broca’s Area: named after the French surgeon and anthropologist Paul Broca, who discovered this area of the brain, Broca's Area is located in the frontal lobe of the brain and acts as the speech centre. Although there are other areas of the brain that also influence speech (Wernicke's Area and the motor cortex), Broca's Area is considered the central component. Curie Marie 1867/1934 Physicist, chemist Cerebellum: the part of the brain controls voluntary muscle movements. that Cerebral cortex: the outer matter of the brain. grey layer of Cerebrum: the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thought, learning, and many other complex activities. It is divided into the left and the right cerebral hemispheres that are joined by corpus callosum which communicates between hemispheres. Cranium: the top of the skull. It protects the brain. The cranium and the facial bones form the skull. Cerebrospinal: fluid, it is a liquid found within the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Corpus callosum: is a wide, flat bundle of neural fibers beneath the cortex in the eutherian brain at the longitudinal fissure. It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitates inter-hemispheric communication. Cortical Homunculus: a cortical homunculus is a pictorial representation of the anatomical divisions of the primary motor cortex and the primary sensorial cortex. Dotti Andrea 1938/2007 Psychiatrist Dura mater: a tough translucent membrane that protects the brain and spinal cord. Dendrites: the branchial structure of a neuron that receives messages. Diencephalon: is the region of the embryonic vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. It is made up of four distinct components: 1. thalamus 2. sub thalamus, 3. hypothalamus, and 4. epithalamus. Einstein Albert 1879/1955 Physicist Epithalamus: its function is the connection of the limbic system to other parts of the brain. Freud Simund 1856/1939 Psychoanalyst Frontal Lobe one of the four subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. The frontal lobe has a role in controlling movement and in the planning and coordinating of behaviour. Giovanni Guglielmini 1763/1817 Physicist Ganglion: an encapsulated collection of nervecell bodies, usually located outside the brain and spinal cord. Grey Matter: portions of the brain that are grey in colour because they are composed mainly of neural cell bodies, rather than myelinated nerve fibers, which are white. Growth Cone: A distinctive structure at the growing end of most axons. It is the site where new material is added to the axon. Heinrich Herzt 1857/1894 Physicist Hypothalamus: a complex brain structure composed of many nuclei with various functions, including regulating the activities of internal organs, monitoring information from the autonomic nervous system, controlling the pituitary gland, and regulating sleep and appetite. Hippocampus: a seahorse-shaped structure located within the brain and considered an important part of the limbic system. One of the most studied areas of the brain, it is involved in learning, memory, and emotions. Issel Arturo 1842/1922 Scientist Interneuron: a neuron that exclusively signals another neuron. Levi Montalcini Rita 1909/2012 Neurologist Limbic System: the part of the brain bordering on the corpus callosum: concerned with basic emotion, hunger, and sex. Marconi Guglielmo 1874/1937 Engineer Medulla: part of the brain stem important for breathing, respiration and other behaviours. Meninges: the three membranes that envelop the brain and the spinal cord. Motor Neuron: a neuron that carries information from the central nervous system to muscle. Myelin Sheath: compact fatty material that surrounds and insulates the axons of some neurons and accelerates the transmission of electrical signals. Newton Isaac 1642/1727 Physicist Nerve: any of the cordlike bundles of fibers that conduct sensory or motor impulses between the brain or spinal cord and another part of the body. Neurotransmitter: a chemical messenger that brain cells use to communicate with one another. Neuron: a nerve cell specialized for the transmission of information and characterized by long, fibrous projections called axons and shorter, branchlike projections called dendrites. Node of Ranvier: of an axon. short unmyelinated segment Oort Jan 1900/1992 Astronomer Occipital Lobe: one of the four subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. The occipital lobe plays a role in processing visual information. Pasteur Louis 1822/1895 Chemist Parietal Lobe: one of the four subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. The parietal lobe plays a role in sensory processes, attention, and language. Photoreceptor: a nerve ending, cell, or group of cells specialized to sense or receive light. Ryle Martin 1918/1984 Astronomer Retina: membrane in the eye that contains light-sensitive cells. Smith William 1769/1839 Geologist Spinal Cord: The extension of the brain through the vertebral column that primarily functions to facilitate communication between the brain and the rest of the body. Sympathetic Nervous System: a branch of the autonomic nervous system responsible for mobilizing the body's energy and resources during times of stress and arousal. Synapse: the point at which a nerve impulse is relayed from the terminal portion of an axon to the dendrites of an adjacent neuron. Thompson Benjamin 1753/1814 Physicist Temporal Lobe: one of the four major subdivisions of each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex. The temporal lobe functions in auditory perception, speech, and complex visual perceptions. Thalamus: a structure consisting of two egg-shaped masses of nerve tissue, deep within the brain. The key relay station for sensory information flowing into the brain, the thalamus filters out information of particular importance from the mass of signals entering the brain. Weinberg Steven 1933 - Physicist White Matter: the part of the brain that contains myelinated nerve fibers. The white matter gets its colour from myelin, the insulation covering nerve fibers. Wernicke's Area: a portion of the left posterior temporal lobe of the brain, involved in the ability to understand words. UDA SCIENCE English Project: «The Human Brain» Students: Marino Laura, Pepe Sara, Luca Cicconetti, Leonardo Marinucci, Emanuele D'Antonio Class: III A Liceo Scientifico Statale «G. Galilei» Pescara A.S. 2013/2014 English teacher: prof.ssa Miscia Roberta