* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 3
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
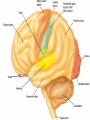
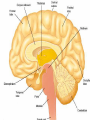
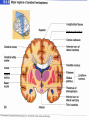
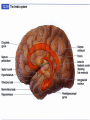
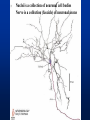
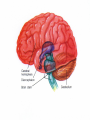
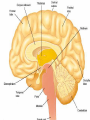
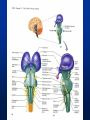
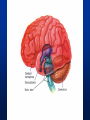
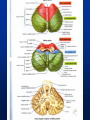
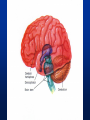
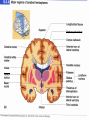
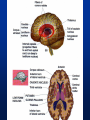
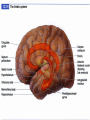
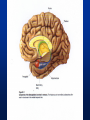
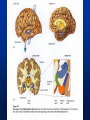
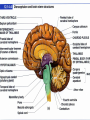
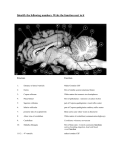
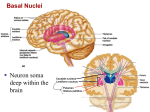
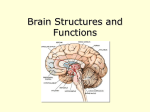
Exam 1 • Moved to the 31 of January Thebrainmcgill • • • • Simple to complex Neurological level Intermediate level Midsagittal view Slides 5, 6, 8, 9 • Could be on test • So be ready to label structures and their functions Brainstem Cerebellum & Deep Structures • • • • • Brainstem: Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Thalamus Cerebellum Basal Ganglia Limbic System Nuclei Collection of neuronal somas in the deeper brain structures Nerves Contain the axons from the neuron cell bodies aka soma Nuclei is a collection of neuronal cell bodies Nerve is a collection (fascicle) of neuronal axons Brainstem • Primitive Part of Brain – Midbrain aka mesencephalon – Pons metencephalon together with cerebellum – Medulla Oblongata myencephalon MIDBRAIN • Functions in visual and auditory orientation reflexes, maintaining posture and voluntary movements of body and face • Contains nuclei for cranial nerves 3, oculomotor; 4, trochlear; 6, abducens • a thoroughfare for axons entering and leaving brain. PONS • Central portion of brainstem • Regulates respiration, thoroughfare for motor and sensory fibers, controls movement of face & jaw muscles, eye movement & sensation to face • Contains nuclei for cranial nerves: 5, trigem; 7, facial • Trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear nerves run through it Medulla Oblongata • Caudal portion of brainstem, leads to spinal cord • Contains nuclei for CN 9-12 involved in speech (tongue & vocal cords), swallowing, move neck & shoulder muscles, salivation, taste • Thoroughfare for afferent & efferent fibers Motor Modulation Systems • Cerebellum • Basal Ganglia CEREBELLUM • derived from hindbrain but not part of brain stem. • connected to pons and medulla by cerebellar peduncles that are made up of axons entering and leaving the cerebellum • 4th ventricle separates it from brain stem. Cerebellum • Major functions – – – – Coordinate muscle activity Posture Equilibrium Spatial Reasoning Function • Motor control for muscle coordination and in planning complicated movements • Cognitive tasks involved in learning and memory of motor task. • Lesions to humans or animals shows that distinct areas of the cb are necessary for spatial reasoning, keeping muscle tone during voluntary movement or reflexes • people can't walk in a coordinated smooth manner after cb lesion ie they appear to walk as if drunk Cerebellar Lobes • • • • Rostral or anterior Caudal or posterior Vermis Flocculonodular • Folia is a term used from gyri in cerebellar cortex that are smaller than in cerebral cortex Deep Cerebellar Nuclei • • • • Emboliform Dentate Globose Fastigial • Are main output neurons from cerebellum Deep Brain Nuclei • Diencephalon: processing sensory & motor information & endocrine role • Basal Ganglia-Striatum: 3 forebrain nuclei involved in motor control • Limbic System: Involved in regulating emotion, motivation & homeostasis DIENCEPHALON • Anterior to midbrain and forms the walls of the third ventricle. • Consists of two parts, the thalamus and hypothalamus – Thalamus: processes sensory info & relays motor info – Hypothalamus: part of limbic system, controls pituitary THALAMUS • Subdividing into 6 nuclei • Relay station for afferent incoming sensory information on the way to the appropriate cortical regions. • Several nuclei in the thalamus receive visual information from the optic nerves • Other nuclei receive auditory information and motor information. HYPOTHALAMUS • involved in maintaining homeostasis, controls body temperature, blood pressure, salt and water levels • initiates and supresses eating, drinking • Activates and inhibits pituitary gland, a neuroendocrine organ • regulates autonomic function such as blood pressure & temperature • involved in emotional responses such as changes in blood pressure/heart rate/respiration, blushing and sweating BASAL GANGLIA • Nuclei surrounding thalamus with common function – 3 components • putamen, globus pallidus, caudate nucleus aka striatum • Substantia nigra • Subthalamic nuclei Deep Brain Nuclei involved in starting and stopping movement Disease to substantia nigra causes parkinson’s disease Function • Function in initiation and planning of voluntary movement and tone of antigravity muscles. Limbic System • Limbic means “border/edge” • Function to – – – – Regulate visceral motor function Emotions , fear irritability depression aggresion Memory Olfaction—food aversions Stop Here Slides 40-43 have details that will not be included in the test. They will be covered during the 2nd half of the course.