* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 4 - Scott County Schools
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
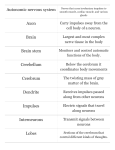
Lesson 20.1: True or False Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. _______ A single neuron may have thousands of dendrites. 2. _______ The cerebellum controls conscious functions such as thinking and speaking. 3. _______ The two hemispheres of the cerebrum are identical to each other. 4. _______ The peripheral nervous system includes all of the nervous tissue in the body except for the brain. 5. _______ The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system prepares the body for emergencies. 6. _______ Seizures in epilepsy are caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. 7. _______ All psychoactive drugs are illegal drugs. Lesson 20.1: Critical Reading Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Read this passage based on the text and answer the questions that follow. The structure of a neuron suits it for its function of transmitting nerve impulses. It has a special shape that lets it pass electrical signals to and from other cells. A neuron has three main parts: cell body, dendrites, and axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles that carry out basic cellular processes. Dendrites receive nerve impulses from other cells. A single neuron may have thousands of dendrites. The axon passes on the nerve impulses to other cells. It branches at the end into multiple nerve endings so it can transmit impulses to many other cells. The nerve endings of an axon don’t actually touch the dendrites of other neurons. Nerve impulses must cross a tiny gap between the two neurons, called the synapse. Chemicals called neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse. When a nerve impulse arrives at the end of an axon, neurotransmitters are released. They travel across the synapse to a dendrite of another neuron. The neurotransmitters bind to the membrane of the dendrite, triggering a nerve impulse in the next neuron. There are three basic types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. All three types must work together to receive and respond to information. Sensory neurons transmit nerve impulses from sense organs and internal organs to the brain via the spinal cord. In other words, they carry information about the inside and outside environment to the brain. Motor neurons transmit nerve impulses from the brain via the spinal cord to internal organs, glands, and muscles. In other words, they carry information from the brain to the body, telling the body how to respond. Interneurons carry nerve impulses back and forth between sensory and motor neurons. Questions 1. Identify the parts of a neuron and their functions. 2. Explain how nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another. 3. Compare and contrast the three basic types of neurons. Lesson 20.1: Multiple Choice Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Circle the letter of the correct choice. 1. Functions of the human nervous system include 1. sensing the internal and external environments. 2. helping maintain homeostasis of the body. 3. preparing the body to fight or flee in emergencies. 4. all of the above 2. How do nerve impulses travel across a synapse? 1. They swim across through synaptic fluid. 2. They are carried across by special chemicals. 3. They jump across like an electric spark. 4. They move across through interneurons. 3. Which statement about the brain is false? 1. It is the most complex organ in the body. 2. It is the largest organ in the body. 3. It consists of billions of neurons. 4. It serves as the control center of the body. 4. Which part of the brain controls involuntary functions such as heartbeat? 1. cerebrum 2. cerebellum 3. brain stem 4. temporal lobe 5. Which part of the peripheral nervous system controls only involuntary responses of the body? 1. sensory division 2. motor division 3. somatic nervous system 4. autonomic nervous system 6. Central nervous system infections include 1. encephalitis. 2. epilepsy. 3. meningitis. 4. two of the above 7. Use of a drug without the advice of medical professionals and for reasons not originally intended is referred to as 1. drug addiction. 2. drug overdose. 3. drug abuse. 4. none of the above Lesson 20.1: Matching Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Match each definition with the correct term. Definitions 1. _______ type of nerve cell that carries nerve impulses back and forth between sensory and motor neurons 2. _______ largest part of the brain 3. _______ part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles 4. _______ part of the brain that controls coordination and balance 5. _______ part of a neuron that receives nerve impulses from other cells 6. _______ part of a neuron that passes on nerve impulses to other cells 7. _______ electrical message carried by neurons Terms 1. axon 2. cerebellum 3. cell body 4. dendrite 5. nerve impulse 6. cerebrum 7. interneuron Lesson 20.1: Fill in the Blank Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Fill in the blank with the appropriate term. 1. A(n) _____ is a bundle of nerve cells. 2. The most common type of brain injury is a(n) _____. 3. Nerve cells that carry messages are known as _____. 4. To pass from one nerve cell to another, a nerve impulse must cross a tiny gap called a(n) _____. 5. _____ neurons transmit nerve impulses from sense organs and internal organs to the brain via the spinal cord. 6. _____ neurons transmit nerve impulses from the brain via the spinal cord to internal organs, glands, and muscles. 7. Loss of sensation and the ability to move, often due to a spinal cord injury, is called _____. Lesson 20.1: Critical Writing Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Thoroughly answer the question below. Use appropriate academic vocabulary and clear and complete sentences. Identify the major parts of the brain, and summarize their functions.