* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuro Anatomy
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
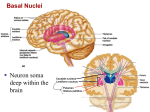
S D U M C K O L A R Structure-function relationships ◦ Localization of function in the CNS Non-invasive brain imaging ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ CAT: structure, low resolution MRI: structure, high resolution PET: function, low resolution fMRI: function, high resolution Functional anatomy ◦ Neural structures that serve particular functions; e.g., pain path from skin to cortex for perception Regional anatomy ◦ Localization of structures in particular brain regions nissl myelin golgi autoradiography Immunohistochemistry In vivo imaging Arc-positive cells after varying amounts of sleep deprivation Neurons ◦ The main information processors Glia ◦ Important supporting roles Astrocytes ◦ support, nurturance Oligodendroglia or Schwann cells •insulation insulation Microglia Represent the immune system in the brain (protect from invasion, clean up debris) cell body nucleus dendrite axon myelin boutons by shape ◦ multipolar, unipolar, bipolar by shape ◦ multipolar, unipolar, bipolar by size ◦ large (pyramidal, eg) ◦ small (granule, eg) by shape ◦ multipolar, unipolar, bipolar by size ◦ large (pyramidal, eg) ◦ small (granule, eg) by function ◦ sensory neuron ◦ motor neuron ◦ interneuron Neurons communicate at synapses synapses can be chemical or electrical, but chemical synapses are more common Synaptic terminology Boutons, cleft, dendritic spines, postsynaptic membrane, vesicles, transmitter, receptors Anterograde vs retrograde microtubules and neurofilaments Anterograde vs retrograde axonal transport Terminology: Afferents and efferents convergence (many:one) and divergence (one:many) nuclei (containers of DNA) and nuclei (collections of neurons) Rostral vs. caudal Dorsal vs. ventral Medial vs. lateral Superior vs. inferior Terminology: Central nervous system (CNS) vs Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Dura mater (tough mother) arachnoid pia mater Major divisions of the brain Sulci and gyri maximize surface area Thalamus ◦ A large mosaic of nuclei which contribute to sensory and motor processing (you’ll meet several of the nuclei later in the course when we look at systems). Hypothalamus ◦ Located just inferior to the thalamus ◦ A collection of nuclei involved in motivated behaviour (feeding, drinking, sexual behaviour) Tectum (roof) ◦ Superior and inferior colliculi Tegmentum (floor) ◦ Some reticular nuclei and cerebellar relay nuclei ◦ Also contains substantia nigra and crus cerebri Cerebellum ◦ A ‘mini’ brain for computing skilled movements and many other things Pons ◦ Many cranial nerve nuclei, reticular nuclei, long tracts Pons (contains cranial nerve nuclei, reticular nuclei) Cerebellum ◦ Many fine folds (folia) increase surface area ◦ Very large # of cells with very tight organization Some nuclei related to breathing, heart rate (so-called vegetative functions) Long tracts How do thought, emotion and behavior arise from this? • Overview of brain anatomy & systems – Localization/networks – Scale in the nervous system – Sensorimotor systems • How our brains interact with the external world (loops) – States ‘of mind’ (and body) • Specific functional systems – Memory & emotion • How our brains use previous experience to modify behavior • Vision & attention; language •Animals & humans: anatomy, physiology, & behavior •Tract tracing •Single unit recordings •Behavioral studies; pharmacology •Patients with focal brain lesions •Behavioral studies & post-mortem anatomy •Structural imaging: In vivo structure/function correlations •Neuroimaging/brain mapping •Functional neuroimaging Phrenology (Gall, early 1800s) 1.The brain is the organ of the mind. 2. The mind is composed of multiple distinct, innate faculties. 3. Because they are distinct, each faculty must have a separate seat or "organ" in the brain. 1860s 1909 2005 Protect by surrounding and buffering Speed transmission by forming myelin sheaths Visual system Visual system Visual system Visual system Visual system Visual system 1909 2005 5 major brain systems subserving cognition and behavior Left perisylvian language network Parieto-frontal network for spatial attention Occipitotemporal network for object/face recognition Medial temporal/limbic network for learning & memory Prefrontal network for attention & comportment From Mesulam MM, Brain, 1998 1) Tubular organization of central nervous system 2) Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal and cranial nerve nuclei 3) Complex C-shaped organization of cerebral cortex and deep structures Tubular organization of central nervous system • Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal and cranial nerve nuclei Nuclei: locations of neuron cell bodies w/in the central nervous system Ganglia: locations of neuron cell bodies in the periphery Tracts: locations of axons w/in the central nervous system Nerves: locations of axons in the periphery Dorsal surface Dorsal root Gray matter White matter Ventral surface Ventral root Spinal nerve NTA 1-4 1) Tubular organization of central nervous system • 2) Columnar/longitudinal organization of spinal and cranial nerve nuclei • 3) Complex C-shaped organization of cerebral cortex and nuclei and structures located beneath cortex – Lateral ventricle – Basal ganglia – Hippocampal formation & Fornix •Portion of the dorsal ectoderm becomes committed to become the nervous system: Neural plate Neural plate Neural groove Neural tube White matter Gray matter Ectoderm Neural tube wall: neurons & glia of CNS Neural tube cavity: ventricular system Neural crest: PNS neurons, etc NTA 3-1 Brain vesicles: Rostral Forebrain Midbrain Neural Tube Development Hindbrain Spinal cord Caudal Rostral neural tube forms the brain Caudal neural tube forms the spinal cord Cephalic flexure NTA 3-2 3-vesicle stage 5-vesicle stage Forebrain Cerebral hemisphere Midbrain Diencephalon Hindbrain Midbrain Pons & Cerebellum Medulla Lateral ventricle 3rd ventricle Cerebral aqueduct 4th ventricle Spinal cord Central canal Cephalic flexure NTA 3-2 …by the 5 vesicle stage, all 7 major brain divisions are present The cephalic flexure persists into maturity Cephalic flexure NTA 1-13 Segmentation • Nuclear organization: columnar Alar plate Sulcus limitans Dorsal horn Central canal Basal plate Ventral horn Dorsal horn Central canal Ventral horn NTA 3-7 Dorsal horn Dorsal root Ventral root Ventral horn Similarities between SC and brain stem development •Sulcus limitans separates sensory and motor nuclei •Nuclei have columnar shape Key differences 1) central canal enlargement motor medial and sensory lateral 2) migration away from ventricle 3) >> sensory and motor Alar plate and migrating neuroblasts Basal plate NTA 3-8 4th Vent Alar plate Striated/branchio. Striated/somite Autonomic. Vestibular/auditory. Somatic sensory. Sulcus limitans Basal plate Taste/viscerosensory Inferior olivary nucleus Alar plate Basal plate NTA 3-9 4th Vent Alar plate Striated/branchio. Striated/somite Vestibular/auditory. Somatic sensory. Taste/viscerosensory Basal plate Sulcus limitans Autonomic. Pontine nuclei Alar plate NTA 3-10 Basal plate Cerebral aq. Alar plate Somatic sensory. Autonomic. Sulcus limitans Basal plate Sub. nigra Striated/somite Red nucleus More like spinal Cord b/c fewer nuclear classes and cerebral aqueduct Basal plate NTA 3-11 Similarities between forebrain and hindbrain/spinal development •Tubular Key differences 1) CH more complex than BS/SC 2) Cortical gyri more complex anatomy than nuclei 3) Subcortical nuclei are C-shaped ◦ Confusing: structure in two places on image Thalamus ◦ Gateway to cortex Hypothalamus ◦ Control of endocrine and bodily functions ◦ Circadian rhythms ◦ Etc. NTA 3-14 Parietal Occipital Frontal Temporal Cerebral cortex (NTA 3-15) Lateral ventricles (NTA 3-16) Striatum (NTA 3-16) Hippocampal formation and fornix (NTA 3-17) 7 Major components of the central nervous system & Ventricles All present from ~ 1st prenatal month • Longitudinal organization of SC and BS nuclei – Columns – Anatomical and functional divisions • C-shape organization of cerebral hemisphere structures and diencephalic – Cerebral cortex – Lateral ventricle – Striatum – Hippocampal formation and fornix